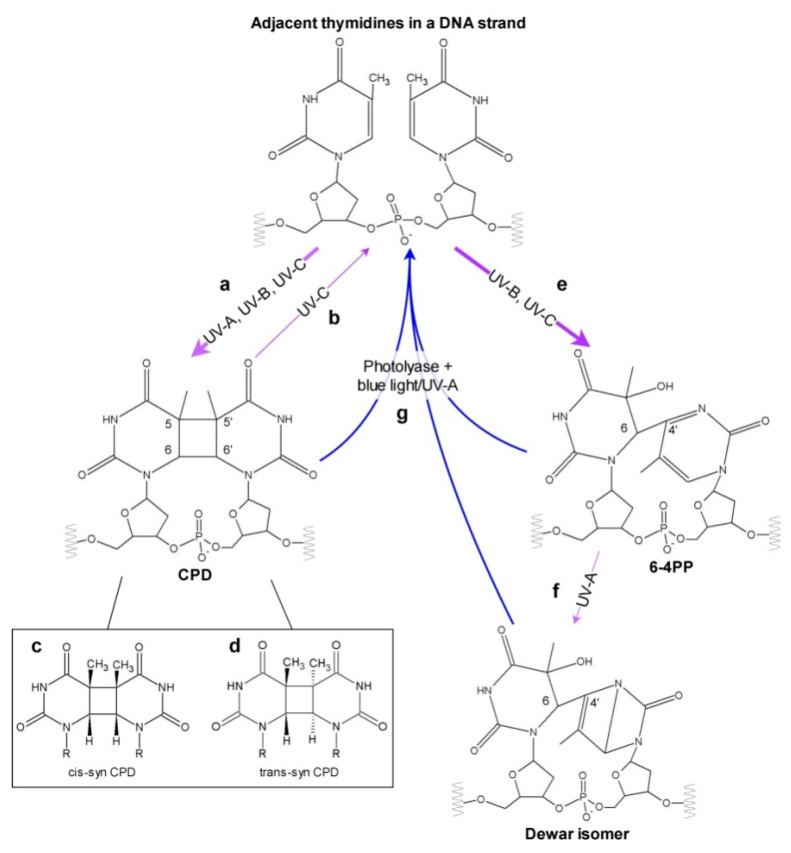
Figure 2.
Diagram showing possible effects of different UV types on neighboring pyrimidines in a DNA strand. Absorption of UV-A, UV-B, UV-C may cause the formation of CPD (a), which can be split back by UV-C (b). Depending on the conformation of the two adjacent bases at the time of irradiation, different CPD stereoisomers can occur—mainly cis-syn CPD (c) and less frequently trans-syn CPD (d). 6-4 PPs are created upon absorption of UV in the UV-B or UV-C range (e), and can subsequently isomerize to Dewar photoproducts in UV-A (f). All three types of photoproducts can be repaired by photoreactivation performed by photolyases requiring blue or UV-A light (g), or by dark repair mechanisms (not shown). Thick and thin purple arrows mark the prevalent and less frequent processes, respectively.