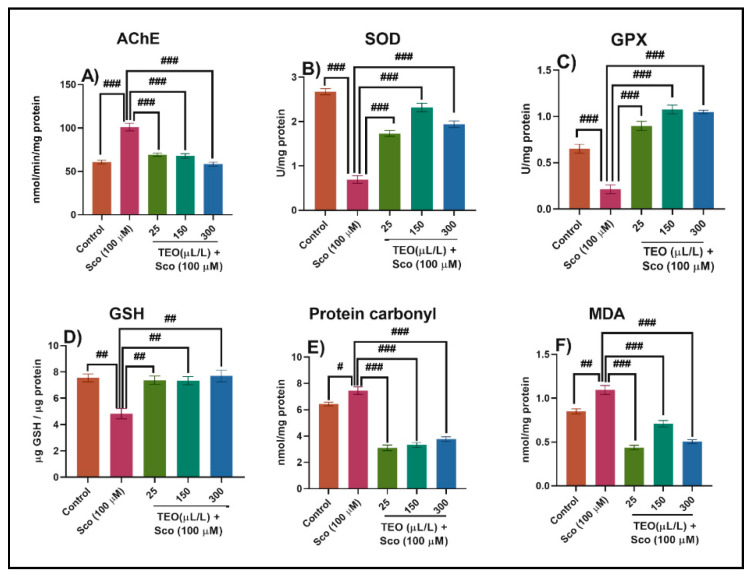
Figure 5.
Thymus vulgaris essential oil (TEO: 25, 150, and 300 μL/L) exhibited an anti- acetylcholinesterase (AChE) effect and improved brain antioxidant status. The enzyme’s specific activities: (A) AChE; (B) superoxide dismutase (SOD); (C) glutathione peroxidase (GPX); (D) reduced glutathione (GSH); (E) protein carbonyl and (F) malondialdehyde (MDA) level. Values are means ± S.E.M. (n = 10). For Tukey’s post hoc analyses: (A) Control vs. Sco (100 µM): ### p < 0.0001, Sco vs. TEO (25 µL/L): ### p < 0.0001, Sco vs. TEO (150 µL/L): ### p < 0.0001 and Sco vs. TEO (300 µL/L): ### p < 0.0001; (B) Control vs. Sco (100 µM): ### p < 0.0001, Sco vs. TEO (25 µL/L): ### p < 0.0001, Sco vs. TEO (150 µL/L): ### p < 0.0001 and Sco vs. TEO (300 µL/L): ### p < 0.0001; (C) Control vs. Sco (100 µM): ### p < 0.0001, Sco vs. TEO (25 µL/L): ### p < 0.0001, Sco vs. TEO (150 µL/L): ### p < 0.0001 and Sco vs. TEO (300 µL/L): ### p < 0.0001; (D) Control vs. Sco (100 µM): ## p < 0.001, Sco vs. TEO (25 µL/L): ## p < 0.001, Sco vs. TEO (150 µL/L): ## p < 0.001 and Sco vs. TEO (300 µL/L): ## p < 0.001; (E) Control vs. Sco (100 µM): # p < 0.01, Sco vs. TEO (25 µL/L): ### p < 0.0001, Sco vs. TEO (150 µL/L): ### p < 0.0001 and Sco vs. TEO (300 µL/L): ### p < 0.0001; and (F) Control vs. Sco (100 µM): ## p < 0.001, Sco vs. TEO (25 µL/L): ### p < 0.0001, Sco vs. TEO (150 µL/L): ### p < 0.0001 and Sco vs. TEO (300 µL/L): ### p < 0.0001.