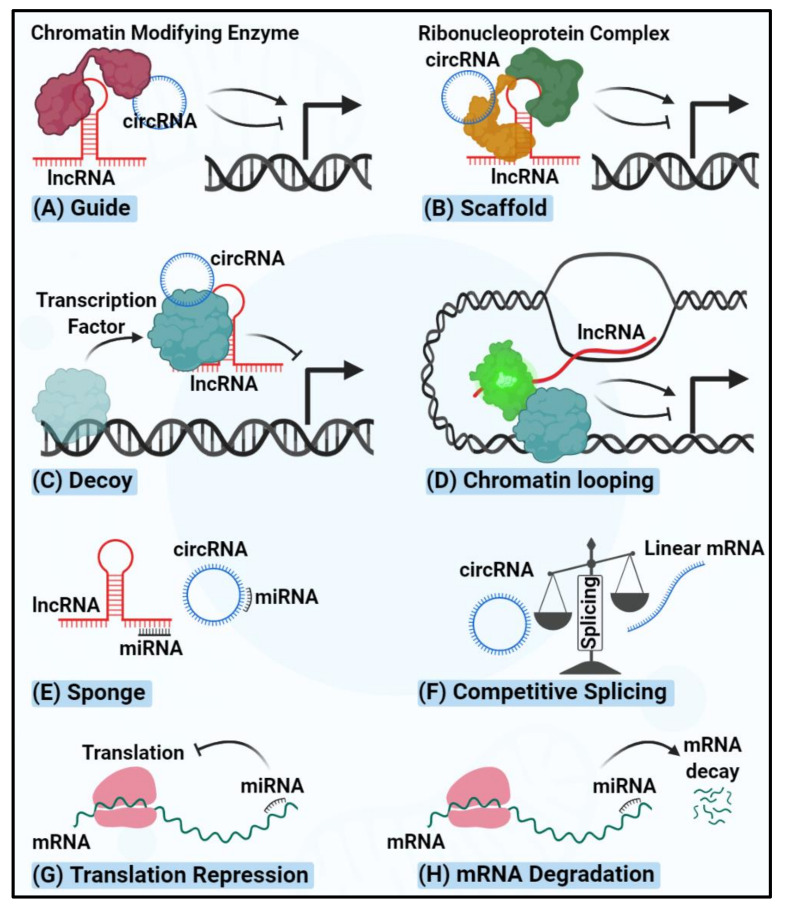
Figure 1.
The schematic of mechanisms of action of ncRNAs. (A) lncRNAs and circRNAs can guide chromatin remodeling factors to either activate or repress the transcription of target genes. (B) lncRNAs and circRNAs, as scaffolds, can facilitate the assembly of ribonucleoprotein complexes to either activate or repress the transcription of target genes. (C) lncRNAs and circRNAs can sponge the transcription factors to repress the transcription of the target genes. (D) Upon transcription, lncRNAs can facilitate the formation of regulatory complexes and loop the DNA, thereby priming long-range gene transcription. (E) lncRNAs and circRNAs can sponge the miRNAs, thereby rescuing the miRNA target transcripts. (F) circRNAs can compete with the linear mRNA(s) transcribed from their host gene and repress the canonical splicing over the back splicing. (G) miRNAs bind to their target mRNAs and repress the translation efficiency upon non-perfect complementation between the seed region and targeted binding site. (H) miRNAs bind to their target mRNAs and result in transcript degradation upon perfect complementation between the seed region and targeted binding site.