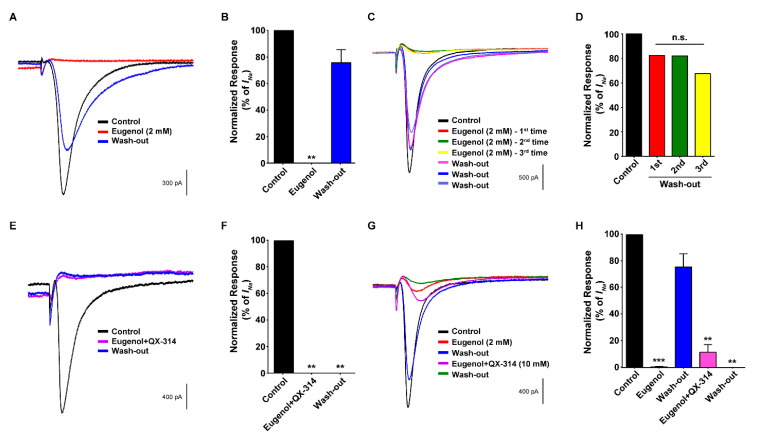
Figure 4.
Effect of co-administration of QX-314 and eugenol on voltage-gated sodium channel currents in small-sized TG neurons. (A) Eugenol alone reduced voltage-gated sodium channel (VGSC) currents, which recovered after wash-out. VGSC currents were measured during 80 ms voltage steps delivered every 3 s from a holding potential of −60 mV to a test potential of 0 mV. (B) The proportion of VGSC current inhibition as a result of eugenol (2 mM, n = 15). (C) The interval (wash-out) time between repeated eugenol treatments (3 times) is at least 5 min. Eugenol (2 mM) inhibited VGSC currents repeatedly. After wash-out, the currents recovered to at least 70% of the control level. (D) The rate of VGSC current recovery after wash-out in TG neurons. The VGSC currents recovered to at least 70% of the control trace. (E) Representative traces of VGSC currents after the co-administration of eugenol and QX-314. QX-314 (10 mM) and eugenol (2 mM) inhibited VGSC currents, which did not recover for at least 40 min after wash-out. (F) The proportion of VGSC currents inhibited by eugenol and QX-314 (n = 8). (G) Eugenol alone and in combination with QX-314 suppressed VGSC currents. Trace showing the effects of eugenol (2 mM; red trace), the combination of eugenol and QX-314 (pink trace), and the control (shown as a black trace) on VGSCs. (H) The proportion of VGSC currents inhibited by eugenol and its combination with QX-314. ** p < 0.01 versus control, *** p < 0.001 versus control and n.s: not significant.