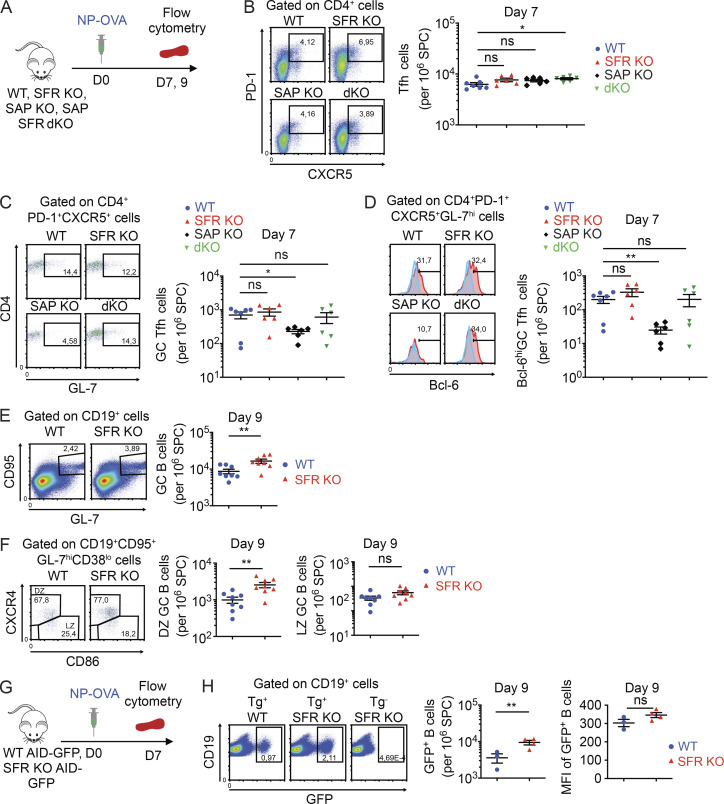
Figure 4.
SFR KO mice display enhanced expansion of the GC reaction. (A–F) As in Fig. 2 B, except that immune cells were detected at the specified times by flow cytometry. The protocol is depicted in A. Tfh cells (B), GC Tfh cells (C), fully committed (Bcl-6hi) GC Tfh cells (D), GC B cells (E), and DZ and LZ GC B cells (F) were enumerated, as specified in Materials and methods. In D, red histograms represent anti–Bcl-6 antibodies, whereas blue histograms represent isotype control antibodies. Bcl-6hi was defined as fluorescence intensity ≥200. For B–D, WT, n = 7; SFR KO, n = 6; SAP KO, n = 6; and SFR SAP dKO, n = 6. For E and F, WT, n = 8; and SFR KO, n = 8. Data are pooled from three independent experiments. (G and H) WT (n = 3) and SFR KO (n = 4) mice were bred with AID-GFP mice, which express the GFP under the control of the AID promoter. The protocol is shown in G. GFP expression in total B cells was determined by flow cytometry (H). Both the percentage of GFP+ B cells (H, middle) and the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of GFP in GFP+ B cells (H, right) are depicted. Data are pooled from two independent experiments. Each symbol represents a mouse. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 (two-tailed Student’s t test). Data are shown as mean ± SEM. For all panels in all figures, representative dot plots, contour plots or histograms are shown on the left, whereas data for multiple independent mice are depicted on the right. Specific populations are boxed or highlighted by horizontal lines. Percentages are shown in the boxes or above the lines. SPC, spleen cells.