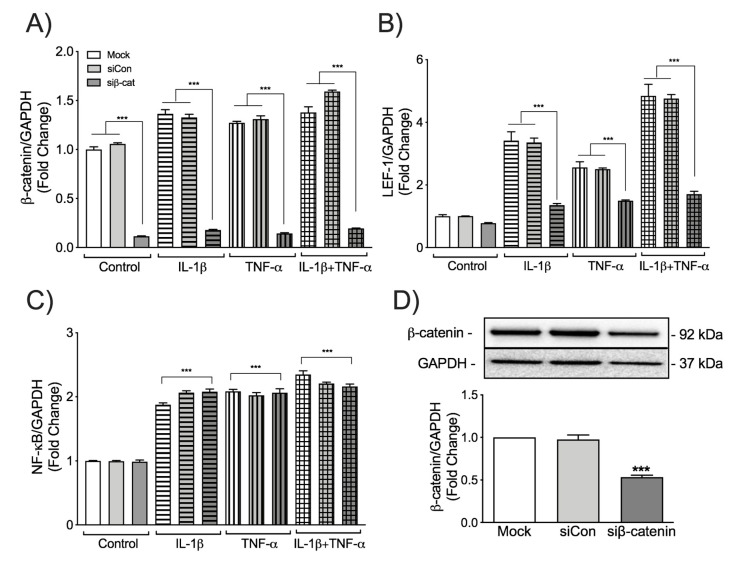
Figure 2.
The effects of β-catenin knockdown on LEF-1 and NF-κB induction in activated human astrocytes. Astrocytes were transfected with either no siRNA (Mock, white bars), non-targeting siRNA (siCon, light grey bars) or siRNA specific for β-catenin (siβ-cat, dark grey bars). Astrocytes were then treated with the HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders (HAND)-relevant cytokines IL-1β (20 ng/mL, horizontal pattern) and TNF-α (50 ng/mL, vertical pattern), alone or in combination (graph check pattern). Total RNA was isolated 8 h post-treatment. (A) β-catenin, (B) LEF-1 and (C) NF-κB mRNA levels were determined by RT-PCR. Data display mRNA fold changes compared to untreated controls. GAPDH was used as a normalizing control. Data are cumulative from three individual astrocyte donors. Statistical analyses were performed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test for multiple comparisons (*** p < 0.001 when compared to Mock or siCon within the treatment). Total protein was isolated 24 h post-treatment and (D) probed for β-catenin. β-catenin levels were quantified by densitometry. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Quantification represents cumulative data from three individual astrocyte donors (*** p < 0.001 when the treatment was compared to Mock or siCon).