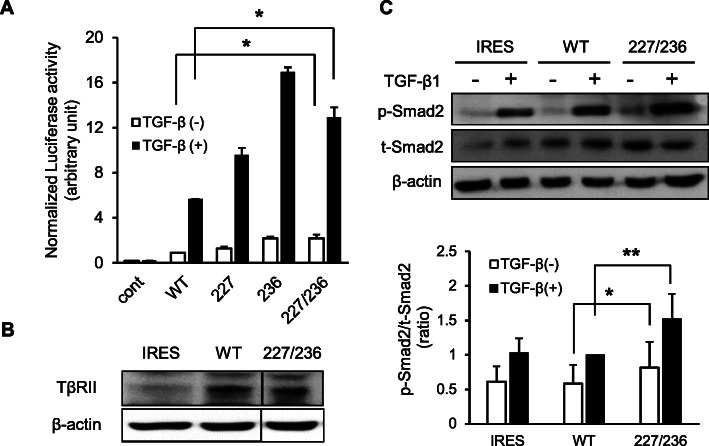
Fig. 1.
Effect of I227T/N236D TβRII mutation on TGF-β signaling. a. Transcriptional activities were assessed via luciferase assay after transfection with pcDNA3 vector (cont), wild-type (WT), I227T (227), N236D (236), and I227T/N236D (227/236) mutant TβRII constructs. DR26 cells were co-transfected with p3TP-lux promoter-reporter construct, pRL-TK, and TβRII constructs. Transfected cells were incubated for 24 h in DMEM supplemented with 0.2% FBS in the presence of vehicle (TGF-β (−)) or 1 ng/ml TGF-β1 (TGF-β (+)). Transfection efficiency was normalized using Renilla luciferase. Data represent mean ± standard deviation (*P < 0.05). b. Stable transfectant cells were constructed by transfection of pIRES2-EGFP vector (IRES), wild-type TβRII (WT), and I227T/N236D TβRII (227/236) constructs into HSC-2 cells. TβRII expression in stable cells was confirmed by western blotting. Protein samples of IRES, WT, and 227/236 were separated on the same gel and the protein bands were cropped. Uncropped blots were shown in Additional file 1: Figure S1. c. Stable HSC-2 cells harboring empty vector (IRES), wild-type TβRII (WT), and I227T/N236D TβRII (227/236) were mock-treated or treated with 10 ng/ml TGF-β1 for 18 h. Smad2 protein level (t-Smad2) and the phosphorylation level of Smad2 (p-Smad2) were determined by western blotting. Data represent mean ± standard deviation from three independent experiments (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). Full length immunoblots were shown in Additional file 2: Figure S2