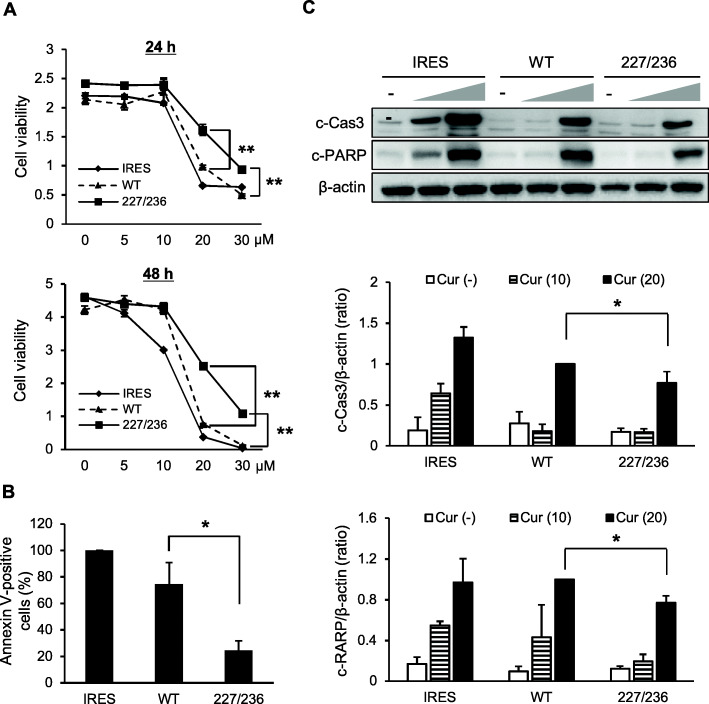
Fig. 4.
Curcumin-mediated apoptotic induction in cells stably expressing exogenous TβRII. a. Stable transfectant cells were cultured with vehicle or varying concentrations of curcumin (5–30 μM) for 24 h and 48 h, followed by MTT assay. Data represent mean ± standard deviation. (**P < 0.01) b. Stable transfectant cells harboring an empty vector (IRES), wild-type TβRII (WT), or I227T/N236D TβRII (227/236) were treated with 20 μM of curcumin for 24 h. Cells were stained with annexin V-FITC and PI, followed by flow cytometric analysis. Bars represent the population of annexin V-positive cells (mean ± standard deviation) (*P < 0.05). c. Cleaved caspase-3(c-Cas3) and cleaved PARP(c-PARP) were analyzed by western blotting. Stable transfectant cells were incubated in P medium containing 0.2% FBS in the presence of vehicle (−) or curcumin (10 and 20 μM) for 24 h. Data represent mean ± standard deviation from three independent experiments (*P < 0.05). IRES, empty vector; WT, wild-type TβRII; 227/236, I227T/N236D TβRII. Full length immunoblots were shown in Additional file 5: Figure S5