Figure 2: The CGG trinucleotide repeats at the 5′-UTR of FMR1cause FXS.
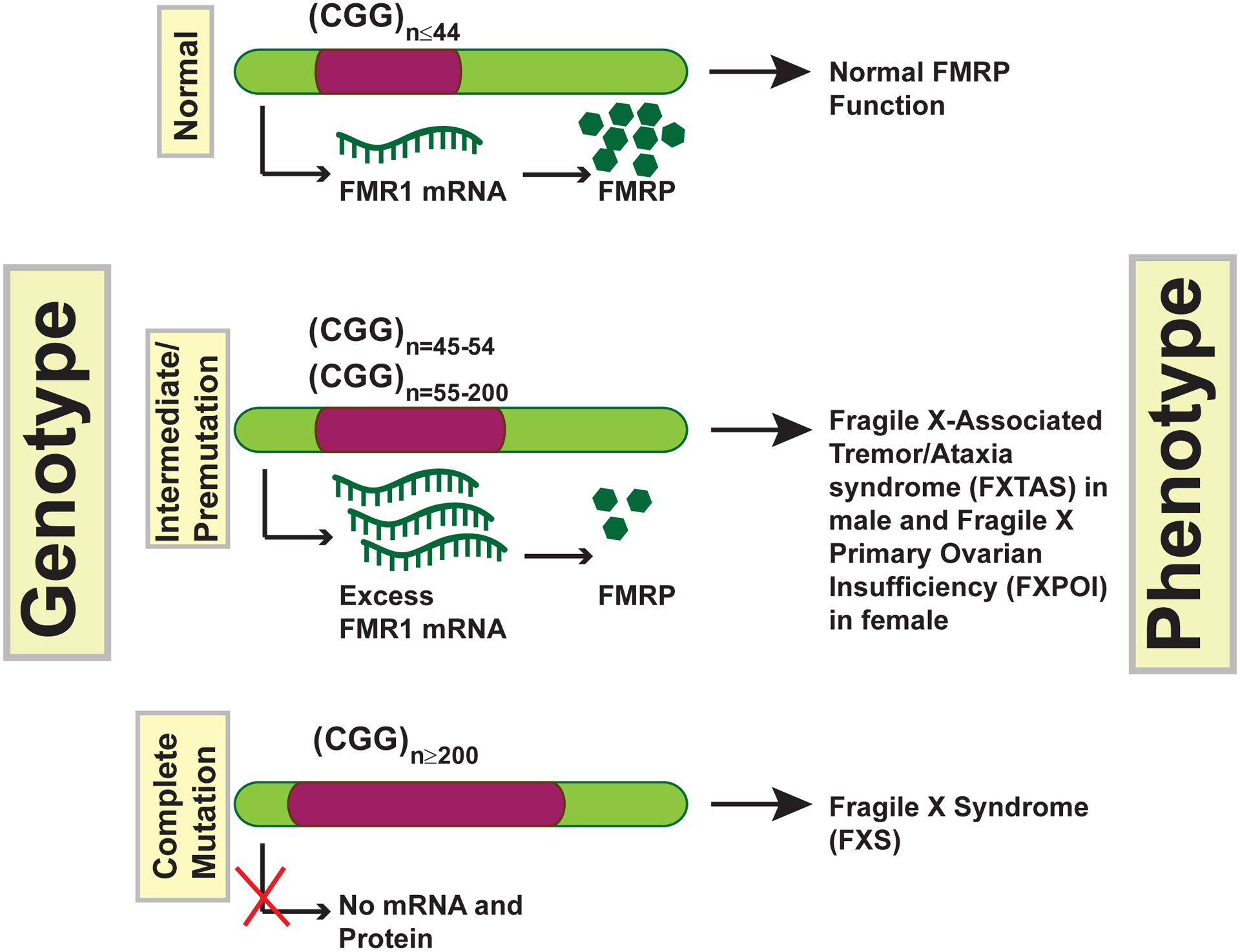
Mutations in the FMR1 gene can lead to several different diseases. Healthy individuals have less than 44 CGG repeats. FMR1 intermediate and premutation carriers can have between 45–54 and 55–200 repeats, respectively. In these cases, FMR1 mRNA is expressed at higher levels than in healthy individuals, although for obscure reasons, FMRP protein levels go down compared to normal due to unclear reasons. These carriers often have an increased chance of developing two disorders, FRAXA in males and FXPOI in females. In cases having more than 200 repeats, the “full mutation,” the FMR1 gene is hypermethylated and silenced, which is the primary cause of FXS.
