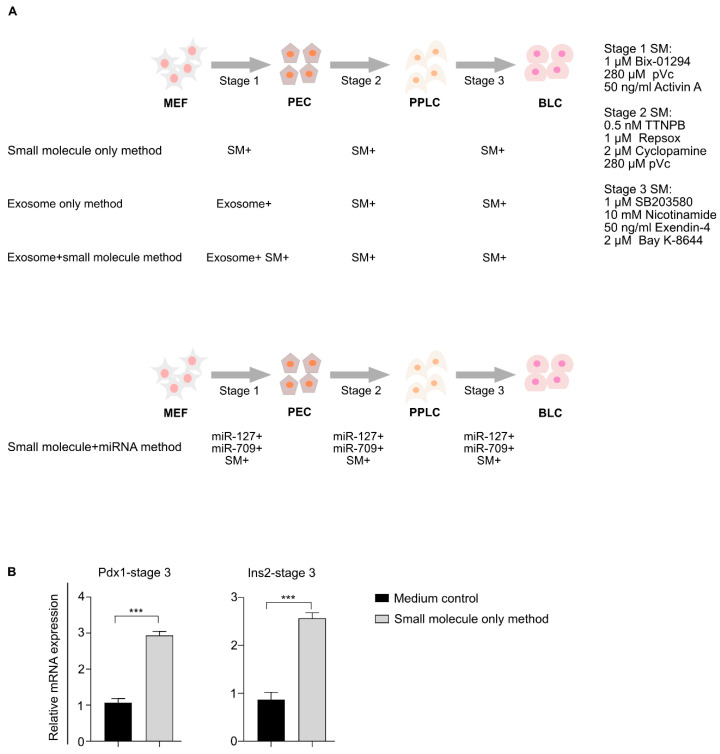
Figure 1.
Development of a chemical-based protocol for mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEF) differentiation. (A) Schematic diagram representing a new small molecule-based method for differentiating MEFs into β-like cells. Additional methods, including exosome only and exosome + small molecule-based differentiation methods, were also investigated. The exosome-enriched miRNAs + small molecule-mediated differentiation approach is depicted in the lower panel. (B) Comparison of pancreatic gene expression in MEFs differentiated using our small molecule only method and medium control cells. *** p < 0.001. Statistical significance was determined by paired, two-tailed t-testing. The data shown represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Complete knockout DMEM was used as the basal medium in all differentiation methods. The medium control cells represent cells grown in basal medium. Stage 1, 2, and 3 media consisted of basal medium + stage 1, 2, and 3-specific small molecules. SM = small molecules, SM+ = addition of small molecules, exosome+ = addition of exosomes, exosome+ SM+ = addition of both exosomes and small molecules, miR-127+ = addition of miR-127, miR-709+ = addition of miR-709, MEFs = mouse embryonic fibroblasts, PECs = pancreatic endoderm cells, PPLCs = pancreatic progenitor-like cells, BLCs = β-like cells, pVc = 2-phospho-L-ascorbic acid, and Ins2 = Insulin-2, ns = non-significant.