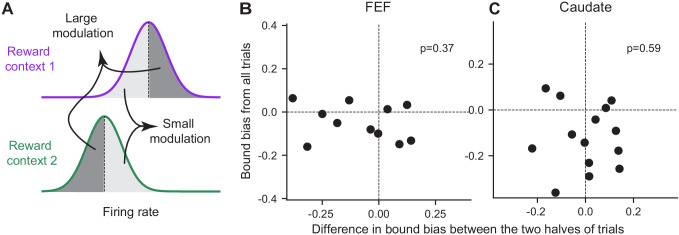
Figure 8. The magnitude of reward bias in relative bound heights did not vary with reward-context modulation of neural activity.
(A) Trials for each reward context were split into two halves based on a neuron’s average activity before motion onset (epoch #3). Reward bias in relative bound heights were measured for trials with large/small reward-context modulation of activity (dark gray/light gray). If the neural activity reflects the behavioral bias, the trials with large modulation were expected to show a larger behavioral bias. (B,C) Scatter plots of the difference in reward bias in relative bound heights between large and small-modulation trials and the bias measured from all trials for FEF (B) and caudate (C) neurons with consistent choice selectivity and significant reward context modulation. P values are from t-test (H0: the mean difference of the x-axis values is zero).