Fig. 3. Manufacturing of heterogeneously integrated e-skin and characterizations of the dynamic linkages at various interfaces.
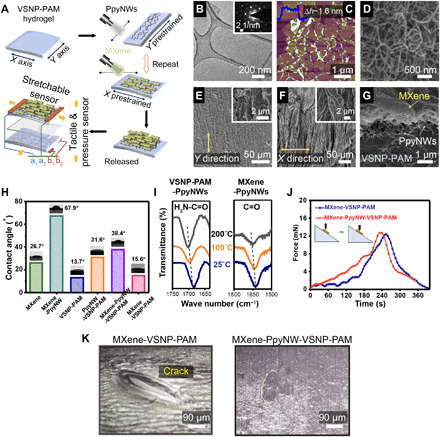
(A) A schematic illustrates the spray-assisted layer-by-layer coating of hydrophobic PpyNW networks between hydrophilic MXene nanosheets for the heterogeneous integration of hierarchically crumpled sensing layers. Morphological characterizations, including (B) TEM (inset is the SAED pattern), and (C) AFM of the MXene nanosheets (scan area: 5 μm × 5 μm), in conjunction with (D) SEM of PpyNWs. Top-view SEM images of PpyNWs and MXene layers with aligned wrinkles and waves formed after releasing the prestretched hydrogel in (E) the y direction and (F) the x direction, respectively. The insets show the higher-magnification SEM images of highly entangled PpyNWs and wrinkled MXene nanosheets. (G) Cross-sectional SEM image of MXene-PpyNW-VSNP-PAM e-skin. (H) Optical images of water droplets on dissimilar composite surfaces and the corresponding contact angles. (I) Temperature-dependent FTIR spectra of VSNP-PAM-PpyNW and MXene-PpyNW upon heating from 25° to 200°C. (J) Mechanical scratch tests carried out to demonstrate the reinforced adhesion between MXene and hydrogel network by introducing PpyNWs. (K) Corresponding optical images of their surface after scratch testing.
