Figure 7. Extracellular Wnt Signal Overrides Physical Contact Cues to Control EMS Division Axis.
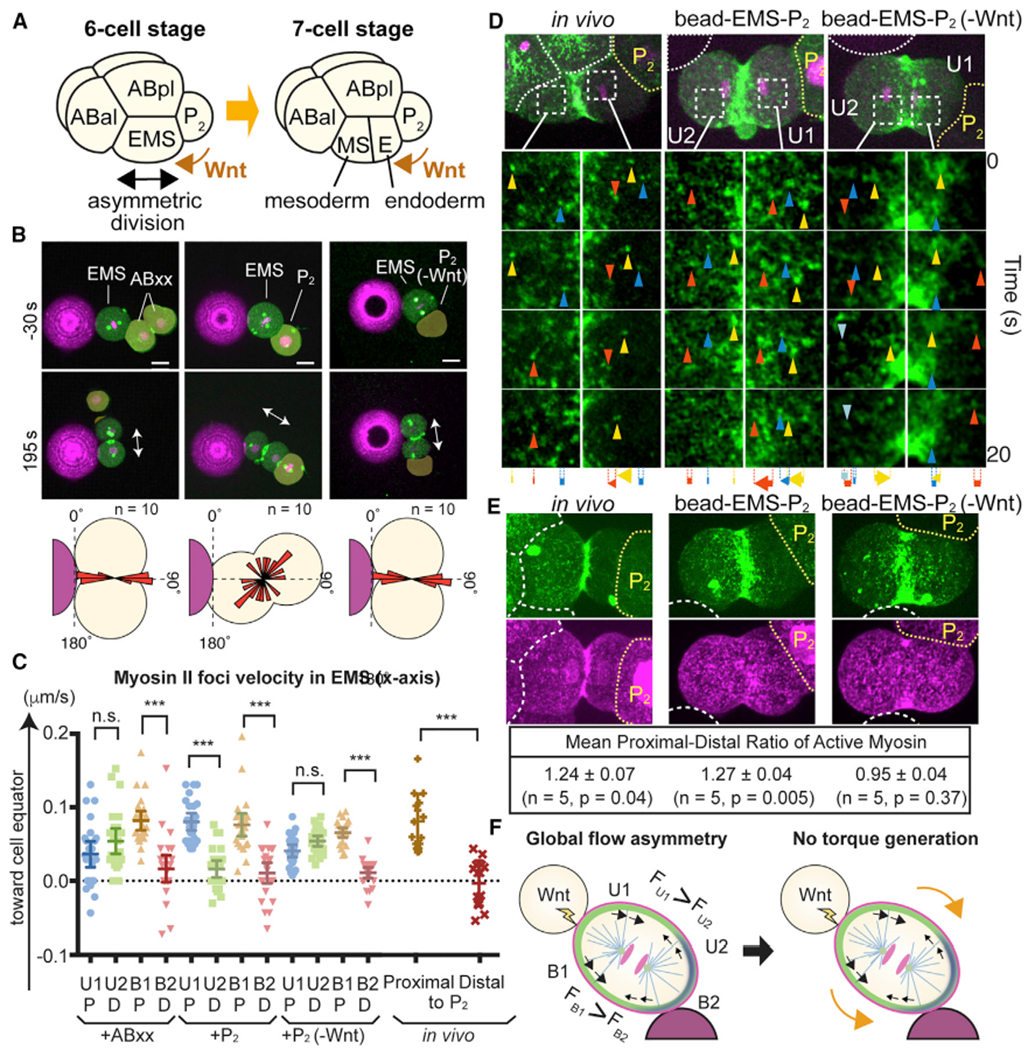
(A) Asymmetric EMS division at the six-cell stage is oriented toward P2 cells despite the presence of multiple physical contact cues.
(B) Bead contact cue blocked by Wnt signal from P2 cell. Myosin (green), centrosomes (green), histones (magenta), beads (magenta), and EMS division axis (arrows) are shown. P2(-Wnt) indicates P2 cells isolated from Wnt(−) mutants. Bottom panel shows the distributions of cleavage furrow orientations.
(C and D) Myosin foci velocities (C) and movements (D) during EMS division. Arrowheads and arrows indicate myosin foci and their total displacement, respectively. Cell quadrants were determined by bead contact site as in Figure 5. P, cell halves proximal to P2 cell; D, cell halves distal to P2 cell.
(E) Wnt-dependent in vivo and in vitro polarization of active myosin localization. Myosin (green), p-RLC (magenta), cell or bead boundaries (white dotted lines), and P2 cells (yellow dotted lines) are shown. Active myosin level was determined as the ratio of p-RLC to myosin intensity.
(F) Model of Wnt-dependent overriding of physical contact cue (see text). Myosin (black arrows) and cell surface (orange arrows) movements are shown.
p values were determined by one-way ANOVA with Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparisons test in (C) and by a paired t test in (E). ***p < 0.0001; n.s., not significant (p > 0.05). Error bars indicate the mean ± 95% confidence interval. Scale bars, 10 μm. See also Figure S6.
