Figure 10.
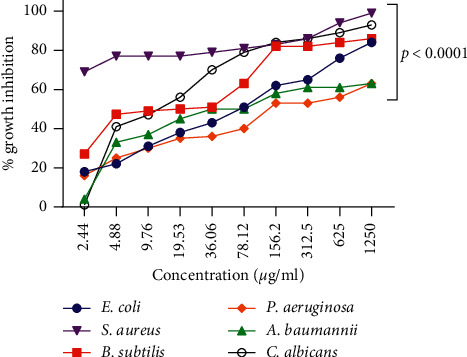
The growth inhibition happened by S. officinalis-mediated ZnO-NP concentrations against Gram-positive strains (B. subtilis and S. aureus), Gram-negative strains (A. baumannii, E. coli, and P. aeruginosa), and C. albicans. This diagram showed that the S. officinalis-synthesized ZnO nanoparticles showed a powerful antibacterial effect for S. aureus and a weaker effect on P. aeruginosa.
