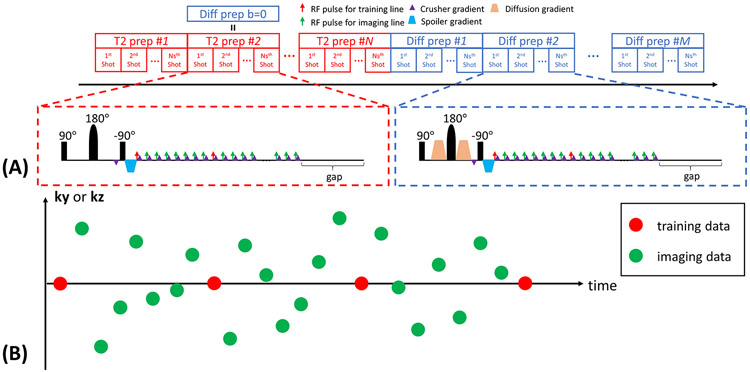
Figure 1.
(A) The sequence diagram of the Multitasking framework. A series of T2preps with different durations are concatenated with a series of diffusion-preparations with different b-values and directions. The duration of one of the T2prep matches the duration of the diffusion prep, so that this T2prep also serves as a b=0 diffusion prep. The crusher gradient scheme is used to avoid tipping inconsistent phase errors onto the longitudinal magnetization and maintain the magnitude consistency by complete dephasing before the tip-up pulse and subsequent rephasing immediately before each readout. A 3D segmented FLASH readout is used for data acquisition. A gap is placed immediately prior to each preparation to allow sufficient signal recovery. (B) The k-space sampling illustration. Imaging data are collected using 3D random Cartesian trajectory with Gaussian variable density along phase encoding (ky) and partition encoding (kz) direction. Subspace training data are collected every 8 readouts for temporal subspace estimation.