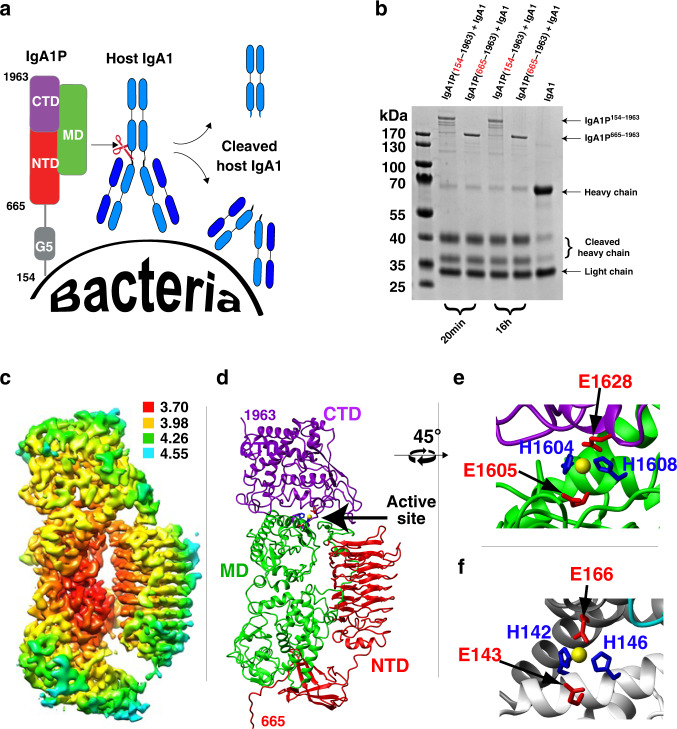
Fig. 1. Function and cryo-EM structure of the S. pneumoniae IgA1P.
a The family of IgA1Ps cleave host IgA1 at its hinge region, separating the IgA1 Fc from its Fab and effectively masking bacterial cells with host IgA1 Fab. The general domain architecture of mature S. pneumoniae IgA1P consists of a flexible N-terminal region (residues 154–664) attached to the bacterial cell wall, which includes a small G5 domain followed by a large C-terminal catalytic region (residues 665–1963)21,22. b S. pneumoniae IgA1P cleavage is similar between the mature IgA1P 154–1963 and isolated catalytic region of IgA1P 665–1963. Shown is one of two independent SDS-PAGE gel measurements. c 3D reconstruction of S. pneumoniae IgA1P (residues 665–1963) is colored according to the local resolution estimates (units in Å). The map was produced using Chimera38. d S. pneumoniae IgA1P ribbon structure highlights the tertiary structure (PDB ID: 6XJB). Domains are each color-coded along with the modeled Zn ion placed based on the superposition of catalytic residues with those found in thermolysin (yellow, arrow). The structure was modeled using Coot32. e Expansion of the S. pneumoniae IgA1P active site with H1604, E1605, H1608, and E1628 shown. f Expansion of the thermolysin active site in a similar orientation to panel E (PDB ID: 1TLX). Functionally homologous thermolysin and IgA1P catalytic residues have the same color coding between panels e and f.