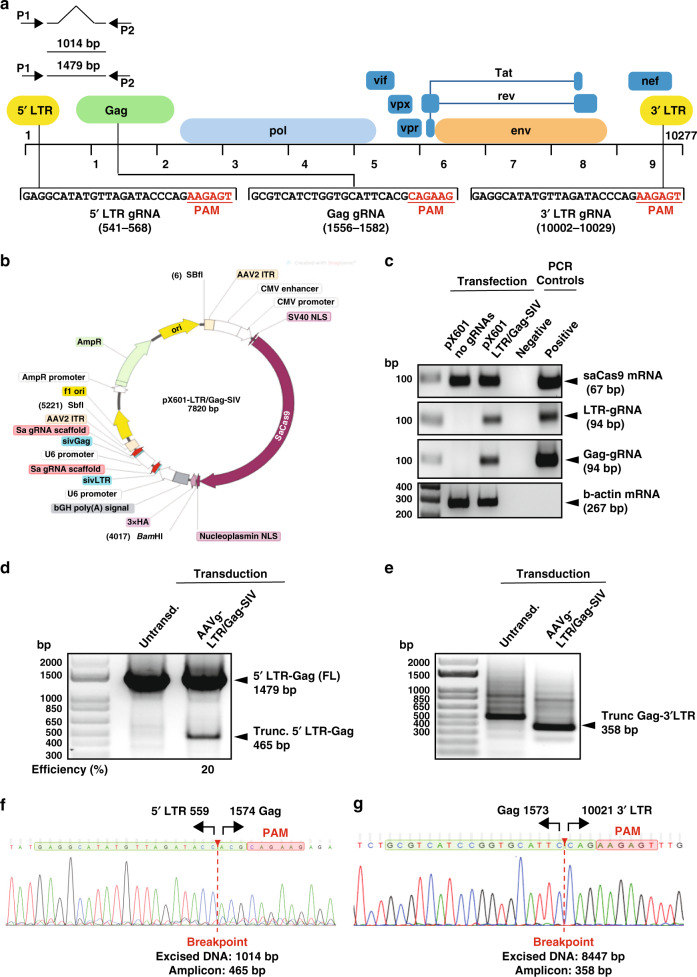
Fig. 1. Construction, map and confirmation of the CRISPR-Cas9 construct targeting SIV proviral DNA in vitro.
a Schematic presentation of the full-length SIVmac239 genome (GenBank: M33262.1) with positions of targeted sites, predicted cleavage events and gRNAs sequences. b Map of AAV pX601-SaCas9-2xgRNA plasmid. c Confirmation of the expression of the plasmid SaCas9 and gRNAs. RT-PCR analysis of SaCas9 and gRNA expression in HEK293T cells transfected with the plasmid. d Gel electrophoresis analysis of PCR reaction for detection of SIV DNA after the treatment of cells with AAV9 delivering CRISPR-Cas9. Results from the PCR analysis showed a clear band of 465 bp in size in the cells that received the CRISPR-Cas9 by infection with AAV9 expressing CRISPR-Cas9. The percent excision efficiency (Efficiency (%)) in vitro shown under the PCR was calculated by quantification of the excised band (trunc.) divided by the sum of the full-length (FL) plus the excised bands times 100%. e Results from the PCR analysis showed a clear band of 358 bp in size in the cells that received the CRISPR-Cas9 by infection with AAV9 expressing CRISPR-Cas9. f Results from the sequencing of the 465 bp amplicon showed the breakpoint of the viral DNA, where the truncated 5′LTR is joined to the residual Gag gene after the removal of the 1014 bp DNA. g Results from the sequencing of the 358 bp amplicon showed the breakpoint of the viral DNA, where the truncated gag is joined to the residual 3′LTR after the removal of the 8447 bp DNA. Full sequencing data are available in the source file data provided with this paper. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.