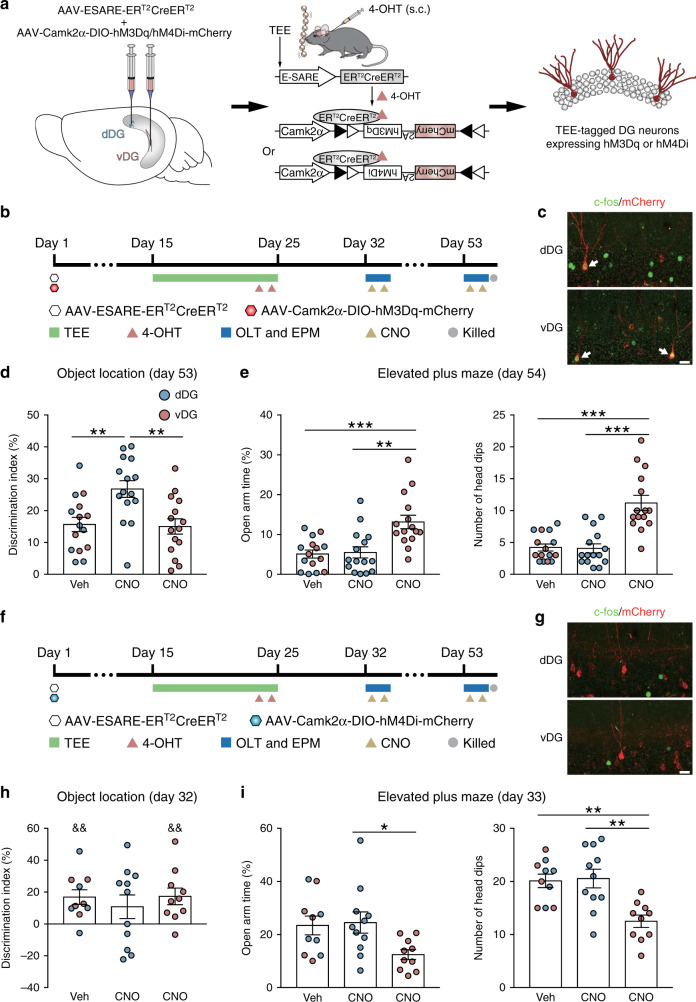
Fig. 6. Effects of chemogenetic manipulation of TEE-tagged dDG or vDG neurons on memory and anxiety.
a Illustration of the strategy to express hM3Dq or hM4Di in TEE-tagged dDG or vDG neurons for chemogenetic manipulation. b The timeline of the chemogenetic activation experiment. CNO, clozapine-N-oxide. n = 15 mice per group. c Representative images from the dDG-CNO group (upper panel) and the vDG-CNO group (lower panel) show c-fos and mCherry immunostaining in dDG and vDG respectively. Arrows indicate activated granule cells that were labeled during tactile enrichment. Scale bar = 20 μm. d, e At 4 weeks after tactile enrichment, chemogenetic activation of TEE-tagged dDG but not vDG neurons enhanced performance in the object location task (d), whereas activation of TEE-tagged vDG but not dDG neurons increased the time in open arms and the number of head dips in the elevated plus maze (e). f The timeline of the chemogenetic inhibition experiment. n = 10–11 mice per group. g Representative images show the absence of colocalization between c-fos and mCherry in dDG or vDG after CNO administration. Scale bar = 20 μm. h, i At 1 week after tactile enrichment, mice with inactivation of TEE-tagged dDG but not vDG neurons failed to discriminate the objects, indicative of impaired spatial memory (h). Inactivation of TEE-tagged vDG but not dDG neurons reduced the time in open arms and the number of head dips in the elevated plus maze (i). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. &&P < 0.01 for pairwise comparisons between the percentage of time exploring the relocated and the stationary objects. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Detailed statistics are provided in Supplementary Table 2. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.