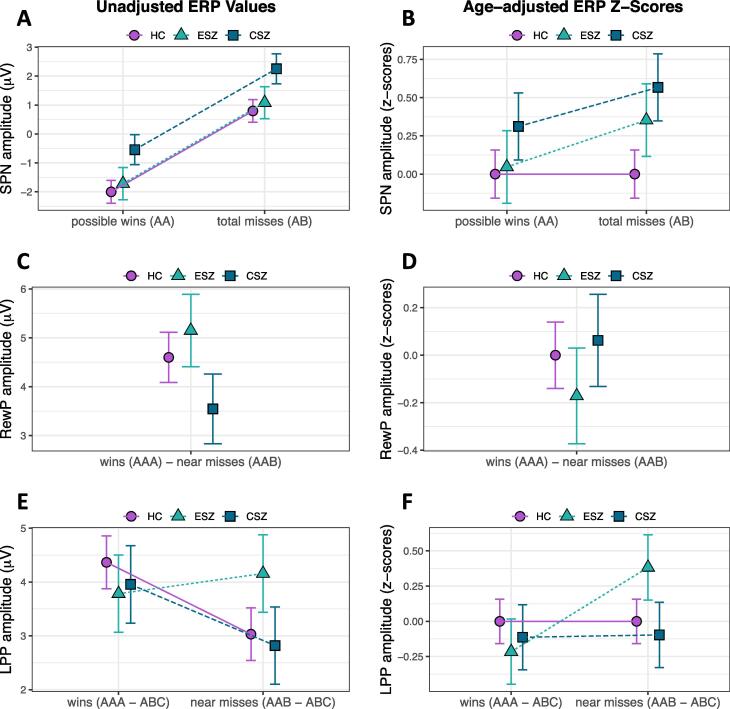
Fig. 3.
Group ERP effects. Results depicting group differences for the three ERPs; group means ± standard error. (A) Stimulus preceding negativity (SPN) Condition effect for possible wins versus total misses regardless of Group (HC, healthy controls; ESZ, early illness schizophrenia subjects; CSZ, chronic illness schizophrenia subjects). (B) No Group × Condition interaction for age-adjusted SPN z-scores. (C, D) No Group differences for Reward Positivity (RewP) unadjusted or age-adjusted z-scores. (E, F) Significant Group × Condition interaction for late positive potential (LPP); whereby the ESZ group showed a heightened LPP response to near misses as compared to wins (F) when adjusting for HC age-related variance. For SPN analyses, we removed two SZ subjects with an average SPN value on AB trials more than 3 SD above the mean; for the LPP analyses, we removed four SZ subjects with average LPP win (AAA – ABC) or near miss (AAB – ABC) values ± 3 SD from the mean. Note for age-adjusted data: data were adjusted to account for normal aging effects using a z-scoring procedure based on a HC age regression model; as a result, HC z-scores have mean = 0 and SD = 1, and the patient groupmeans reflect the degree and direction of abnormality, in standard units, from the HC-derived norms.