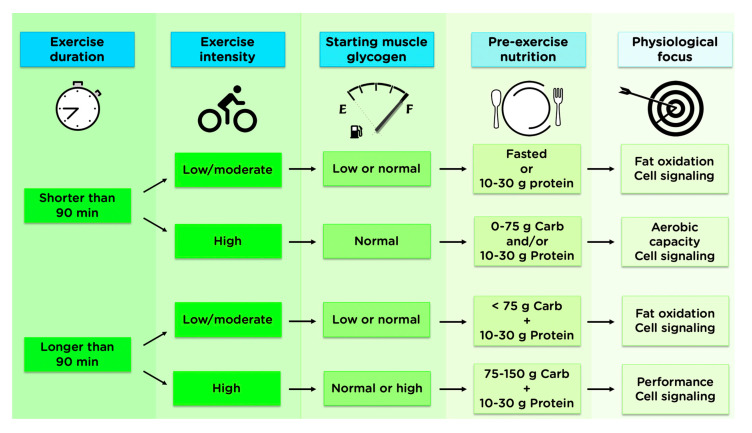
Figure 9.
Practical application of pre-exercise nutrition to optimize training adaptations. The duration and intensity of the exercise session should be considered when considering the best pre-exercise nutrition choices. Before shorter duration exercise sessions that focus on lower intensity steady-state training, it may be beneficial to withhold CHO, while there is little evidence supporting CHO restriction before high-intensity exercise. When consuming less than ~75 g CHO, food choices before HIIT can be left to personal preference. For longer duration exercise (>90 min), there is little evidence to suggest fasted-state training offers any additional benefit, although this is still practiced by approximately one-third of endurance athletes [16]. Ingesting less than ~75 g CHO is unlikely to impair mitochondrial signaling adaptations from longer-duration, low-intensity exercise, while consuming 75–150 g CHO prior to extended high-intensity exercise is suggested to increase endogenous fuel storage.