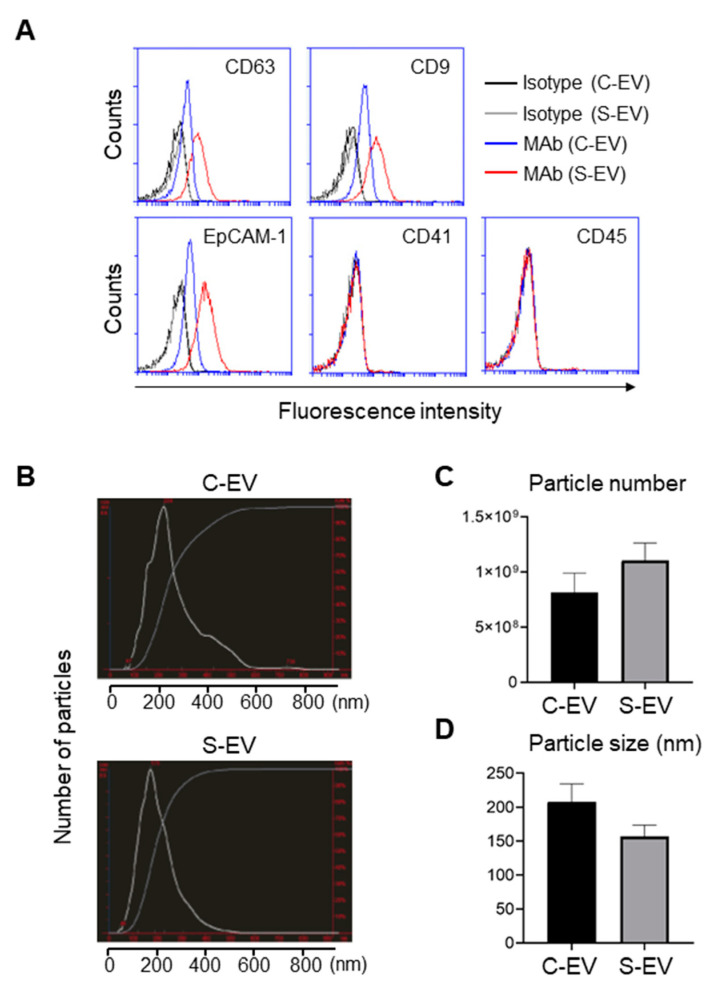
Figure 1.
Characterization of EVs isolated from luminal washes in large intestines of control and septic mice. (A) Flow cytometry analysis of EVs isolated from luminal washes in large intestines of control and sepsis mice. EVs were isolated by differential UC and adsorbed on 4 μm poly-L-lysine microbeads overnight. Immobilized EVs (20 μg) were stained with indicated monoclonal antibodies (MAb) and subjected to flow cytometry to evaluate their expression. Representative histograms show changes in expression of indicated marker. Black line, isotype (C-EV); gray line, isotype (S-EV); blue line, MAb (C-EV); and red line, MAb (S-EV). (B) Representative NanoSight LM10 images showing sizes of EVs from control (top) and septic (down) mice. (C) Particle number of EVs as quantified by NTA. (D) Size distribution of gut- derived C-EVs (N = 15) and S-EVs (N = 16) mice groups as measured by dynamic light scattering (DLS) device. C-EV, control extracellular vesicle; and S-EV, sepsis extracellular vesicle.