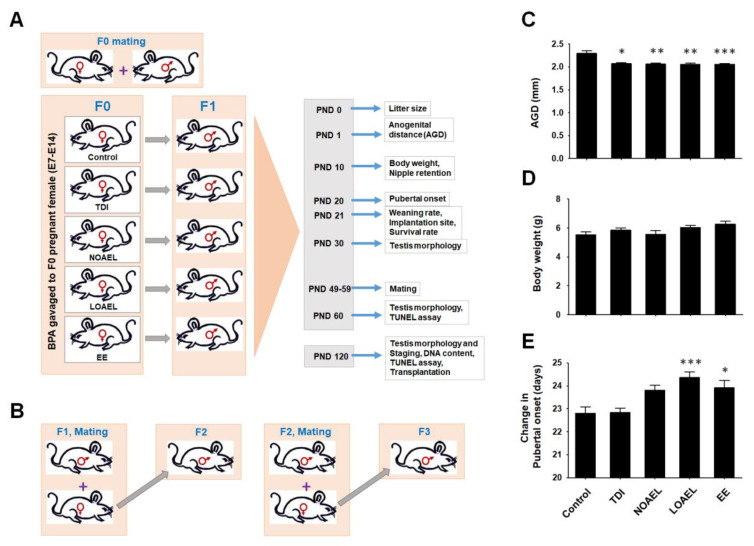
Figure 1.
Experimental design (A,B), anogenital distance (C), body weight (D), and pubertal onset changes (E) in F1 male offspring. (A) After mating, pregnant female mice were gavaged with different bisphenol A (BPA) doses [tolerable daily intake (TDI) (50 µg/kg bw/day), no-observed-adverse-effect-level (NOAEL) (5 mg/kg bw/day), and lowest-observed-adverse-effect-level (LOAEL) (50 mg/kg bw/day); see detailed dose description in text], control (corn oil), and positive control (ethynylestradiol; EE). (B) Mating scheme to produce descendants (F1 to F3 generation). Age-matched nontreated females were used (PND 49–59). No inbreeding was performed. (C) Anogenital distance (AGD) of F1 male pups at PND 1, measured in millimeters. (D) Body weight of F1 male pups at PND 10, measured in grams. (E) Changes in days of pubertal onset for F1 offspring. Data (C–E) were generated from 23 male offspring per group. Data analyzed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) where asterisk (*) indicate significant differences compared with control (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001).