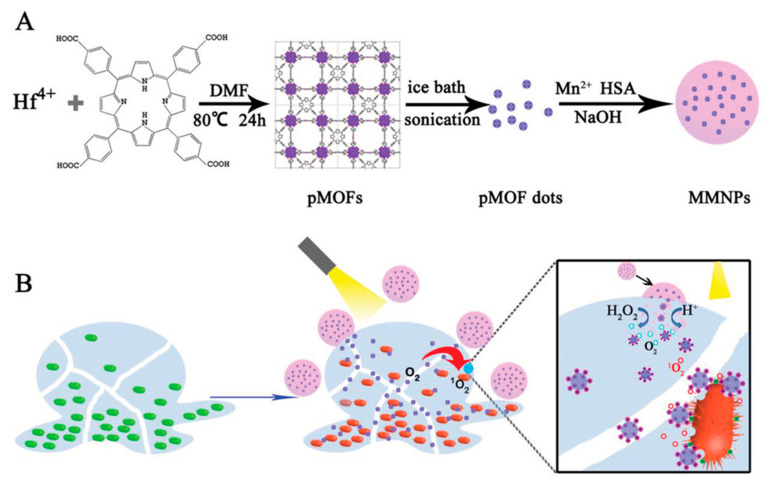
Figure 7.
(A) Schematic illustration of nanomaterial fabrication for a multi-component nanoplatform (MMNPs) containing porphyrin-containing metal–organic framework (pMOF) dots. (B) Schematic of the mechanism of bacterial biofilm treatment by the nanoplatform (MMNPs) and external activation by NIR light. The MMNPs decomposed under an acidic environment, causing MnO2 degradation and pMOF dot release. The pMOF dots were then activated by NIR light to produce the reactive oxygen species. Additionally, in the presence of H2O2, MnO2 catalyzed H2O2 to form O2, enhancing the photodynamic therapy (reproduced from [75] with permission from John Wiley and Sons, 2019).