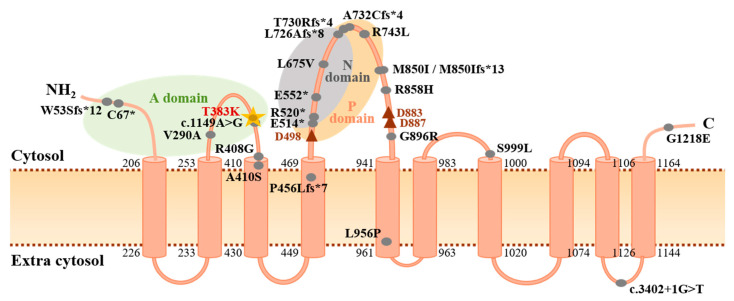
Figure 2.
Protein structure of ATP13A3 highlighting mutations identified in PAH. Topological analysis of ATP13A3 according to UniProtKB protein component and site position data (ID: Q9H7F0) and published reports [38,40]. Likely pathogenic PAH mutations (CADD ≥ 15) reported in the literature are indicated by the filled grey circles [10,12,20,41]. The c.1148C>A (p.T383K) mutation identified in this study is highlighted by the gold star and is located adjacent to a previously reported splice-region variant [10]. Numbers indicate amino acid positions at each end of the 10 transmembrane domains. The red triangles denote essential asparagine residues (D498: active catalytic site; D883, D887: Mg2+ binding sites). A domain: actuator domain; C: carboxyl terminus; N domain: nucleotide binding domain; NH2: amino terminus; P domain: phosphorylation domain.