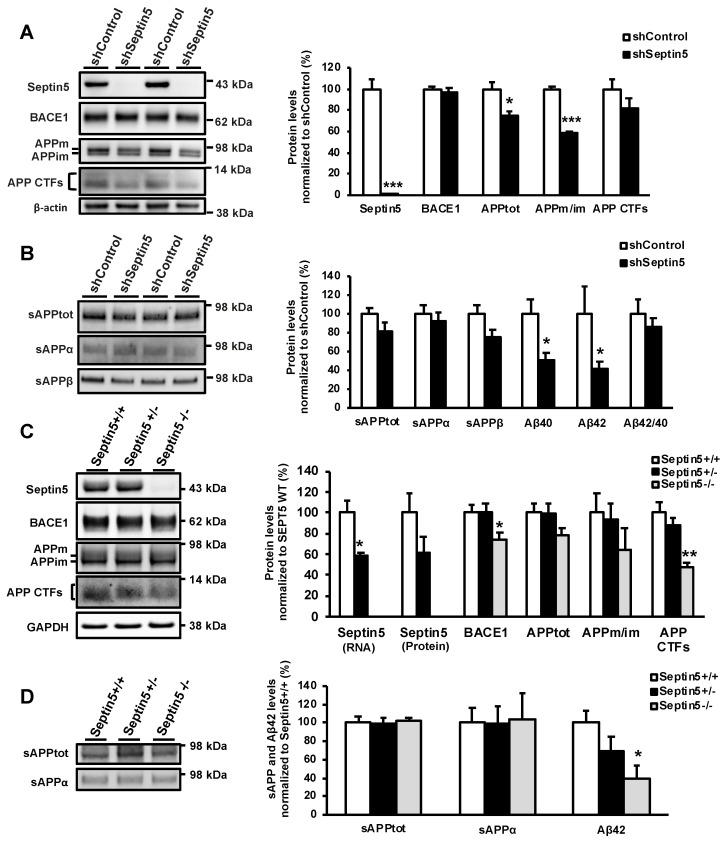
Figure 2.
Downregulation of SEPTIN5 affects APP processing and the levels of Aβ in primary mouse cortical neurons and Septin5 knockout mice. (A) Western blot analysis showing a significant downregulation of mouse Septin5 and the ratio of APPm/im in mouse primary cortical neurons transduced with lentiviral Septin5 shRNA; (B) Aβ40 and Aβ42 levels (ELISA) are significantly decreased in mouse primary cortical neurons after the downregulation of Septin5 as compared with the control-transduced neurons. n = 4; (C) Western blot analysis of ventral cortical protein lysates from five-month-old Septin5+/+, Septin5+/−, Septin5−/− mice. The levels of BACE1 and APP CTFs were significantly reduced in Septin5−/− mice. Septin5+/+ (n = 5), Septin5+/− (n = 5), Septin5−/− (n = 4); (D) Analysis of sAPPtot, sAPPα, and Aβ levels in the temporal cortex of Septin5+/+, Septin5+/−, Septin5−/− mice. The levels of Aβ (ELISA) were significantly reduced in Septin5−/−, but not in Septin5+/− mice, suggesting that the effects of Septin5 downregulation on Aβ were dose dependent. Septin5+/+ (n = 7), Septin5+/− (n = 7), Septin5−/− (n = 3). In (A, C) protein levels were normalized to β-actin and GAPDH, respectively, and are shown as a % of siControl/Septin5+/+, mean ± SEM. In (B) and (D), protein levels were normalized to total protein levels in the respective cell lysates and are shown as a % of siControl/Septin5+/+, mean ± SEM. A/B, independent t-test. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. C/D, one-way ANOVA post hoc LSD. * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01.