Figure 2. LD Accumulation of LiveDrop Requires Specific Sequence Features.
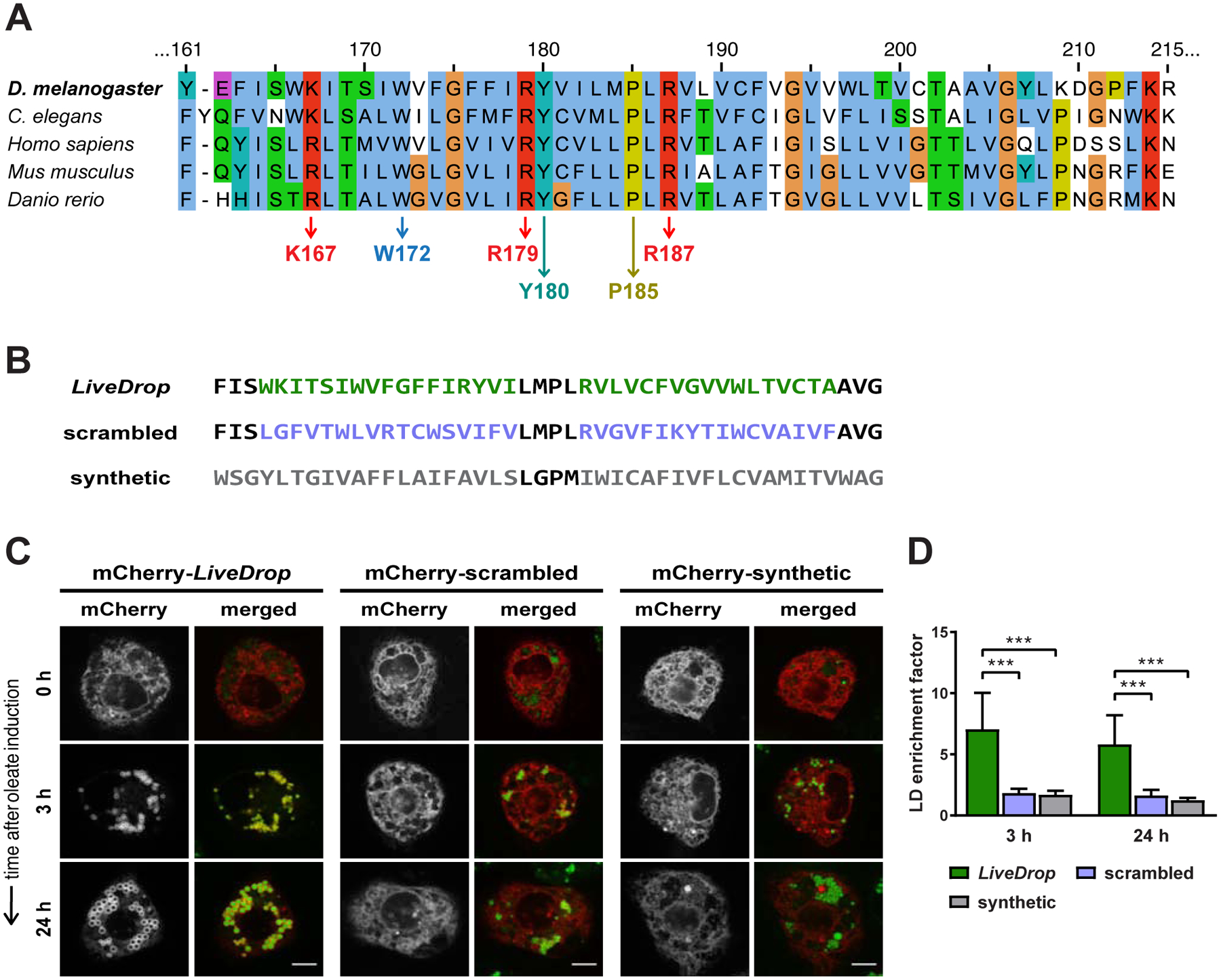
(A) Sequence alignment of the D. melanogaster LiveDrop motif (160–215 aa) and other GPAT4 ortholog sequences from representative species. Conserved residues are highlighted, including P185 (dark yellow), positively charged residues (K167, R179, R187, red), and large hydrophobic residues (W172, Y180, sky blue or teal).
(B) Amino acid sequences of LiveDrop (green), a scrambled LiveDrop variant (violet), and a synthetic hydrophobic α-helical motif (gray).
(C) The scrambled LiveDrop variant and the synthetic hydrophobic motif do not target LDs. S2 cells transfected with mCherry-tagged versions of the protein motifs in (B) (red) were incubated with oleate throughout the indicated time points and imaged by confocal microscopy. LDs were stained with BODIPY (green). Scale bar, 5 μm.
(D) Mean values + SD (n > 12) of the protein signal on LDs after 3 and 24 h of oleate treatment. ***, p < 0.001.
