Figure 4. Positively Charged and Tryptophan Residues Are Required for Efficient LD Targeting of LiveDrop in Cells.
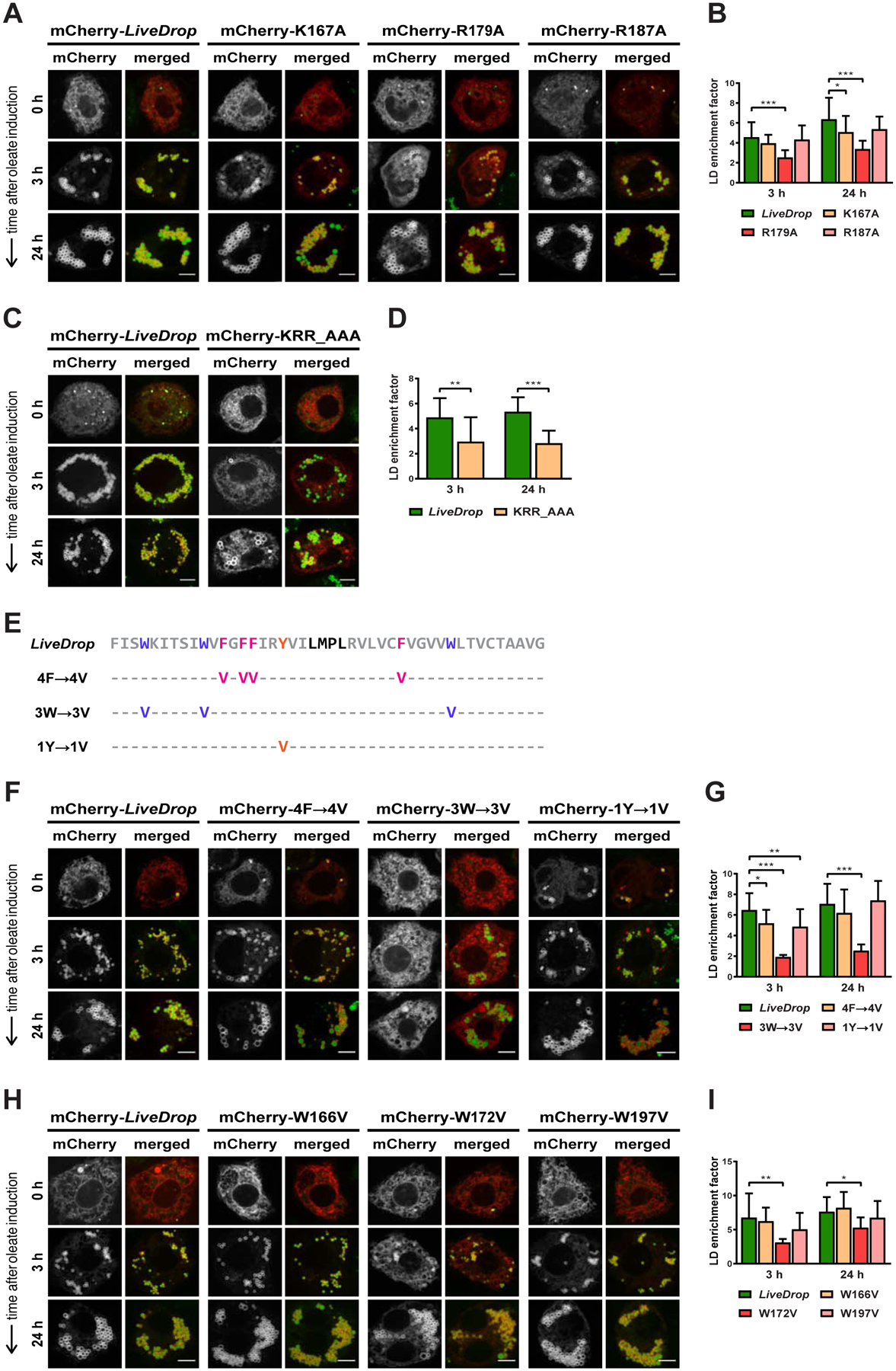
(A) Of the three LiveDrop variants with single positive charge mutations (K167A, R179A, R187A), only R179A causes a reduction in LD accumulation.
(B) Mean values + SD (n > 18) of the protein signal on LDs after 3 and 24 h of oleate treatment. *, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001.
(C) A LiveDrop variant with the three positively charged residues (K167, R179, R187) exchanged for alanines (KRR_AAA) is compromised in LD accumulation to a similar extent as the single R179A mutation.
(D) Mean values + SD (n > 10) of the protein signal on LDs after 3 and 24 h of oleate treatment. **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.
(E) Amino acid sequence of LiveDrop variants in which the phenylalanines (4F→4V, magenta), tryptophans (3W→3V, purple), and tyrosine (1Y→1V, orange) are individually mutated to valines. The predicted hinge of the LiveDrop sequence (gray) is shown in black. For each LiveDrop variant, the amino acid positions indicated with a hyphen (−) remain the same as in the original sequence.
(F) The LiveDrop variant with mutated tryptophans (3W→3V) does not accumulate on LDs, but the variants with mutated phenylalanines (4F→4V) and tyrosine (1Y→1V) target LDs in a manner comparable to the wild-type sequence.
(G) Mean values + SD (n > 10) of the protein signal on LDs after 3 and 24 h of oleate treatment. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.
(H) LiveDrop variants with single tryptophan mutations (W166V, W187V) target LDs similar to the wild-type sequence, except for W172V, which shows reduced LD accumulation.
(I) Mean values + SD (n > 10) of the protein signal on LDs after 3 and 24 h of oleate treatment. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.
For (A), (C), (F), and (H), S2 cells were transfected with mCherry-tagged versions of the LiveDrop variants (red), incubated with oleate throughout the indicated time points, and imaged by confocal microscopy. LDs were stained with BODIPY (green). Scale bar, 5 μm.
