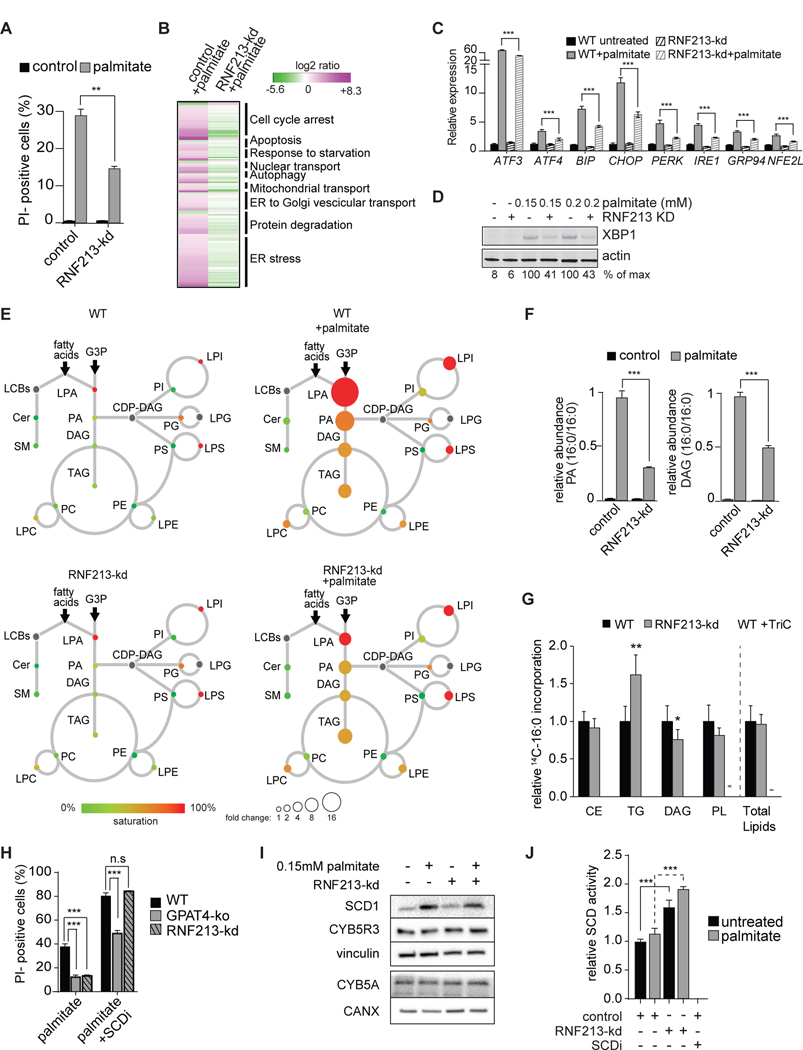
Figure 6. Depletion of the Putative E3 Ligase RNF213 Protects against Palmitate-Induced Lipotoxicity.
(A) Knockdown of RNF213 prevents palmitate-induced cell death. Propidium-iodide staining of control or RNF213-kd cells untreated or treated with 0.2 mM palmitate for 24 h. n=3 for each treatment. **p < 0.01.
(B) Knockdown of RNF213 protects against palmitate-induced activation of the UPR. Left lane, RNAseq data of wild-type K562 cells treated with 0.2 mM palmitate for 20 h. Genes (p<0.005) are shown as log2 ratio of palmitate compared to the control and designated as being upregulated (magenta) or downregulated (green). Right lane, RNAseq data of RNF213-ko K562 cells treated with 0.2 mM palmitate for 20 h. Genes are shown as log2 ratio compared to the control treated with palmitate. The complete dataset is provided in Table S2 “Gene expression profile data”.
(C) Knock-down of RNF213 prevents palmitate induction of UPR target genes. Relative expression of main UPR target genes performed by qPCR. n=3 for each treatment, ***p < 0.001.
(D) RNF213-kd protects cells against palmitate-induced UPR. Western blot of total cell lysate from control and RNF213-kd cells treated with vehicle or palmitate (0.15 or 0.2 mM) for 16 h. XBP1 protein is quantified as percentage over the max signal (100%) detected among all conditions.
(E) Lipidome of control K562 cells treated with palmitate (0.2 mM) for 20 h, as described in Figure 1B. The size of the circles is proportional to the fold-change, compared to untreated control cells. Lyso-phosphatidic acid (LPA) circle size was reduced 16-fold for visualization purposes. The complete dataset is provided in Table 1 “Lipidomics data”.
(F) Knockdown of RNF213 reduces accumulation of palmitate-induced di-saturated lipid species. Relative quantification for phosphatidic acid (PA, left panel) and diacylglycerol (DAG, right panel) identified by LC-MS2. Control or RNF213-kd K562 cells untreated or treated with 0.2 mM palmitate for 24 h. The lipid species changing the most upon palmitate treatment is shown for each class. n=3 for each treatment. ***p < 0.001.
(G) RNF213-kd cells exhibited unaltered total lipid synthesis but increased TG accumulation. Cells were treated for 6 h with 0.2 mM nonradiolabeled palmitate and 0.15uCi 14C-palmitate. Triacsin C (10uM, an inhibitor of ACSL1, ACSL3 and ACSL4) was added to confirm ACSL-specific fatty acid uptake. n=6 for each treatment. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
(H) Inhibition of SCD1 exacerbates palmitate-induced cell death, an effect that is suppressed by GPAT inhibition but not by RNF213 knockdown. Propidium-iodide staining of GPAT4-ko or RNF213-kd cells treated with 0.2 mM palmitate for 20 h with or without SCD inhibitor (4 μM). n=3 for each treatment. ***p < 0.001; n.s., non-significant.
(I) SCD1 and cytochrome B5 reductase (CYB5R3) protein levels are not increased by RNF213 knockdown. Western blotting of total cell lysates from control and RNF213-kd cells untreated or treated for 16 h with 0.15 mM palmitate.
J) SCD activity is elevated in RNF213-kd cells compared to wildtype cells. In vitro Δ9 desaturase activity was determined in microsomes collected from WT and RNF213-kd cells untreated or treated with 0.15mM palmitate for 16 h and was measured as release of 3H from [9, 10-3H]-stearoyl-CoA. SCD inhibitor (4 μM) was included as a control. n=3 for each treatment. ***p < 0.001.
See also Figures S6.