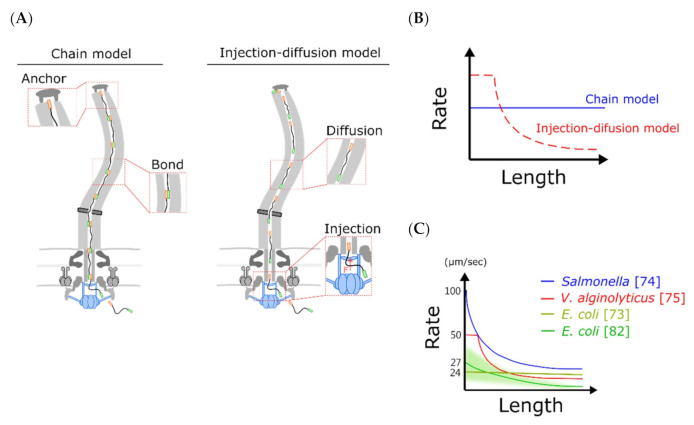
Figure 4.
Potential mechanisms of the flagellar growth process. (A) Schematics of the chain model (left) and the injection-diffusion model (right) are shown. The chain model proposed that sequential flagellins are linked head-to-tail to form a chain, and the first flagellin anchors beneath the distal end of the flagellum to provide a pulling force. Therefore, constant force contributes to a constant growth rate. According to the injection-diffusion model, the secretion system applies a secretion force on an unfolded flagellin, and flagellins are delivered through diffusion after entering the channel. Hence, flagellins are crowded on the channel when the flagellum is getting longer. (B) The chain model predicts a constant growth rate, and the injection-diffusion model predicts a length-dependent growth rate. (C) The summary of flagellar growth rate of three bacteria using fluorescent-based techniques.