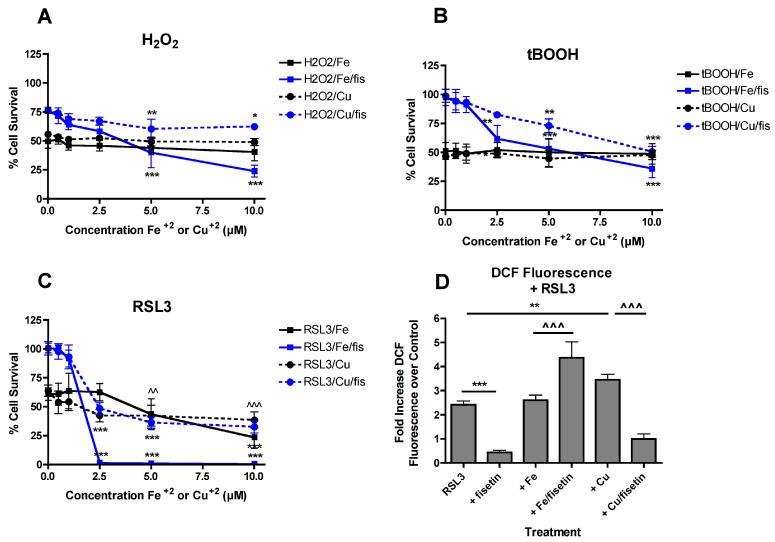
Figure 4.
FeCl2 and CuCl2 modulate the effects of fisetin on protection from multiple toxicities. FeCl2 and CuCl2 reduce fisetin-mediated protection against hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) (A) or t-butyl peroxide (tBOOH) (B) toxicity. HT22 cells were treated with 0.5 mM H2O2 or 2.5 µM tBOOH in the presence of 10 µM fisetin and/or FeCl2 or CuCl2 at the indicated concentrations. Cell survival was measured after 24 h with the MTT assay. The experiments were done in quadruplicate and the results are the average of 4 independent experiments. (C) FeCl2 and CuCl2 differentially affect fisetin-mediated protection against RSL3 toxicity. HT22 cells were treated with 100 nM RSL3 in the presence of 5 µM fisetin and/or FeCl2 or CuCl2 at the indicated concentrations. Cell survival was measured after 24 h with the MTT assay. The experiments were done in quadruplicate and the results are the average of 5 independent experiments. (A–C), * indicates p < 0.05, ** indicates p < 0.01 and *** indicates p < 0.001 relative to fisetin + toxin alone. (C), ^^ indicates p < 0.01 and ^^^ indicates p < 0.001 relative to RSL3 alone for both FeCl2 and CuCl2. (D) Cells were treated with 250 nM RSL3 alone or in the presence of 10 µM fisetin and 5 µM FeCl2 or CuCl2. After 4 h, ROS levels were determined using CM-H2DCFDA as described in Materials and Methods. The treatments were done in sextuplicate and the results are the average of 4 independent experiments. ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 relative to RSL3 alone. ^^^ p < 0.001 relative to RSL3 + FeCl2 or CuCl2 alone.