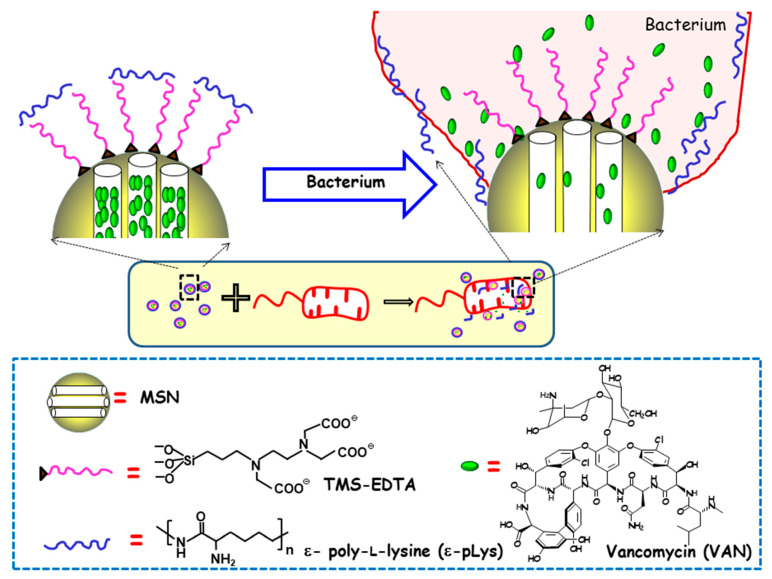
Figure 4.
Schematic depiction of the action mechanism of bacterium-triggered antimicrobial nanosystems was composed of MSNs loaded with vancomycin (VAN), functionalized with N-[(3-trimethoxysilyl)propyl] ethylendiamine triacetic acid trisodium salt (TMS-EDTA) and capped with ε-poly-L-lysine (ε-pLys) in the presence of E. coli. Adapted from ref. [48]. Mesopores capping occurs via electrostatic interactions between cationic ε-pLys and negatively charged TMS-EDTA. In the presence of bacteria, the adhesion of the ε -pLys gatekeeper with the negatively charged bacteria wall triggers pore uncapping and allows cargo release, as schematically shown as an inset.