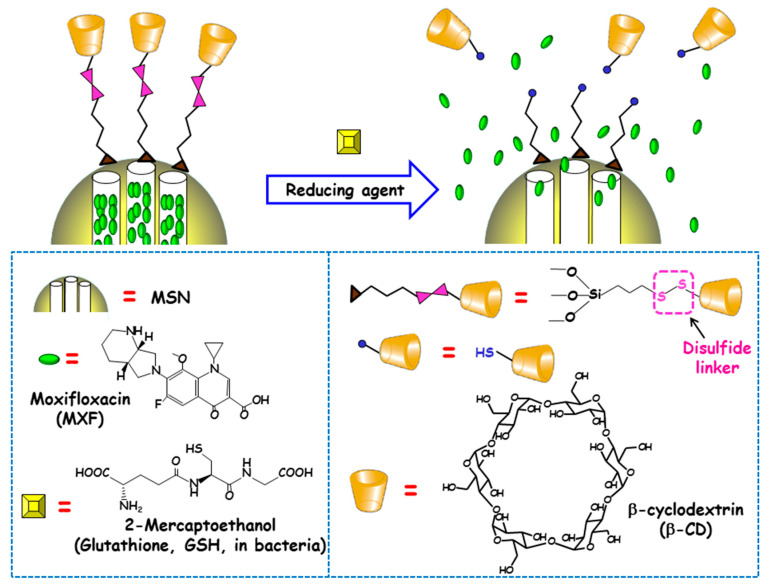
Figure 7.
Schematic depiction of the operating mechanism of redox-responsive antimicrobial nanosystems consisting of disulfide modified MSNs loaded with moxifloxacin (MXF) and end-capped with β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) throughout a disulfide linker. Adapted from ref. [91]. The exposition to reducing milieu in bacteria (e.g. glutathione or 2-mercaptoethanol) triggers the cleavage of disulfide bond, which allows pore uncapping and cargo release.