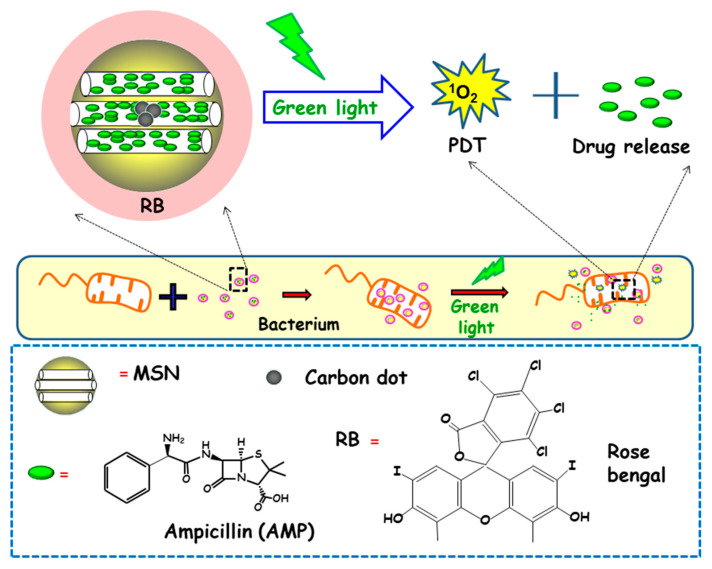
Figure 10.
Schematic depiction of the mechanism of action of antimicrobial light-responsive antimicrobial nanosystems consisting MSNs containing carbon dots (C-dots), rose bengal (RB) and ampicillin (AMP). Adapted from ref. [98]. Upon green light irradiation of nanosystems, the RB photosensitizer triggers the generation of singlet oxygen species (1O2), which produces pore uncapping and AMP release. Synergistic combination of photodynamic therapy (PDT) and antimicrobial release lead to enhanced antimicrobial effect.