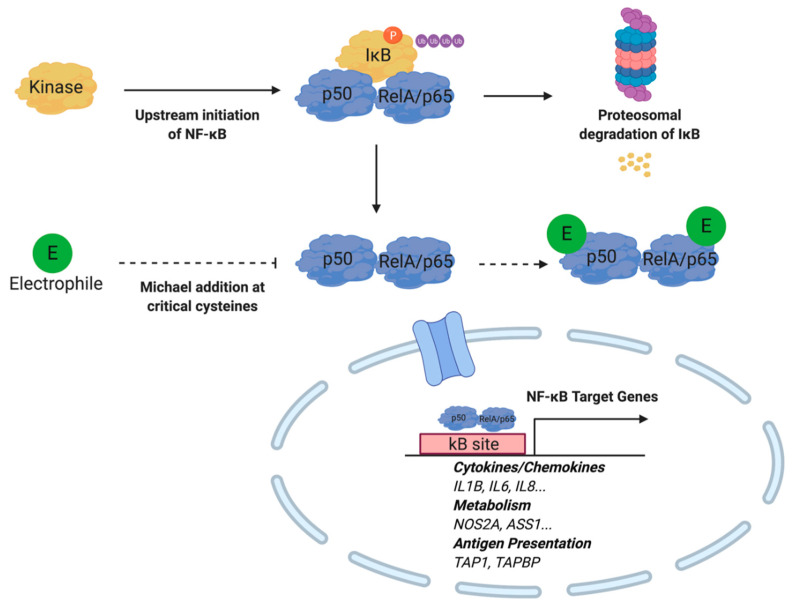
Figure 5.
Electrophiles inhibit NF-κB activity by binding to the p50 and RelA/p65 protein subunits. Michael addition at cysteine moieties prevent nuclear translocation required for target gene expression. Under inflammatory conditions, kinase activity induced by upstream NF-κB signaling results in phosphorylation, ubiquitinylation, and proteasomal degradation of IκB. Subsequently, NF-κB translocates to the nucleus to initiate target gene expression.