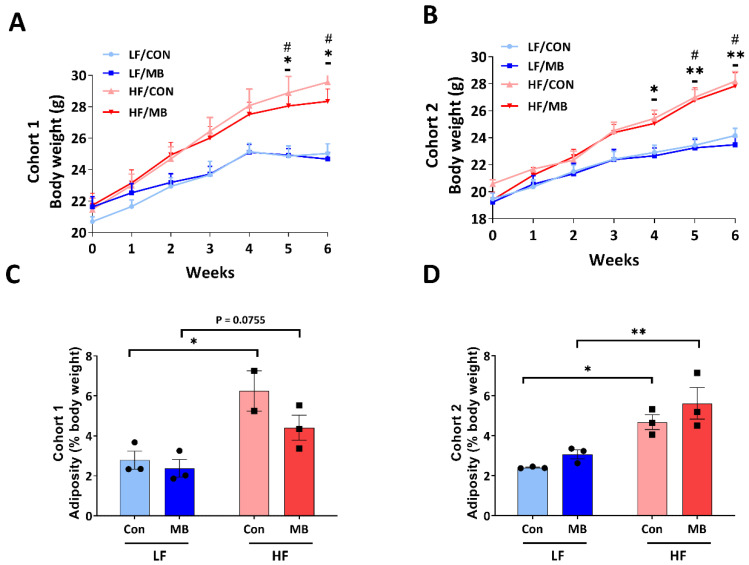
Figure 1.
Effect of monobutyrin (MB) supplementation on body weight (A,B) and adiposity (C,D) in low-fat (LF) and high-fat (HF) fed mice. Cohort 1 (A,C) and cohort 2 (B,D) of mice fed an LF or HF diet with or without 0.25% MB supplementation diet for 6 weeks. Two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s or Sidak’s post hoc test was used to determine differences among groups. Repeated measures ANOVA was performed for body weight on variable clusters with a random subject effect, whereas variable cluster members, diet, and MB treatment were used as fixed effects. Values are means ± standard of error of mean (SEM)s; n = 6 for body weight (gain) and 2–3 for adiposity/group/cohort. Significant differences are denoted as an asterisk (*) for LF/CON vs. HF/CON at * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 and a sharp (#) for LF/MB vs. HF/MB. CON, control; HF, high-fat; HF/CON, HF without MB; HF/MB, HF with 0.25% MB (w/v) in drinking water; LF, low-fat; LF/CON, LF without MB; LF/MB, LF with 0.25% MB (w/v) in drinking water; MB, monobutyrin.