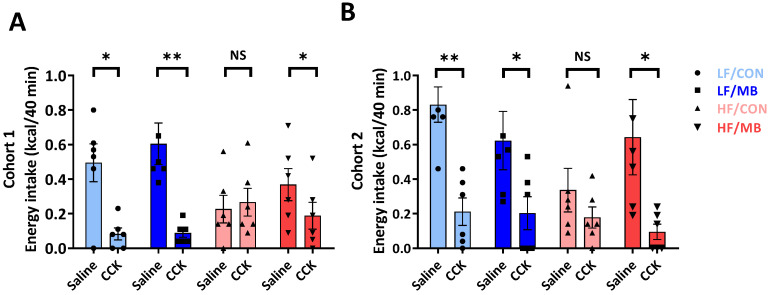
Figure 4.
Effect of MB supplementation on vagally-mediated gut–brain signaling. Cholecystokinin (CCK) sensitivity in cohort 1 (A) and cohort 2 (B) of mice fed an LF or HF diet with or without 0.25% MB supplementation diet for 6 weeks. Paired Student’s t-test was used to determine statistical significance within groups. Values are means ± SEMs; n = 6/group/cohort. Asterisk (*) denotes significant differences among groups at * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01. NS, not significant; CCK, cholecystokinin; HF, high-fat; HF/CON, HF without MB; HF/MB, HF with 0.25% MB (w/v) in drinking water; LF, low-fat; LF/CON, LF without MB; LF/MB, LF with 0.25% MB (w/v) in drinking water; MB, monobutyrin.