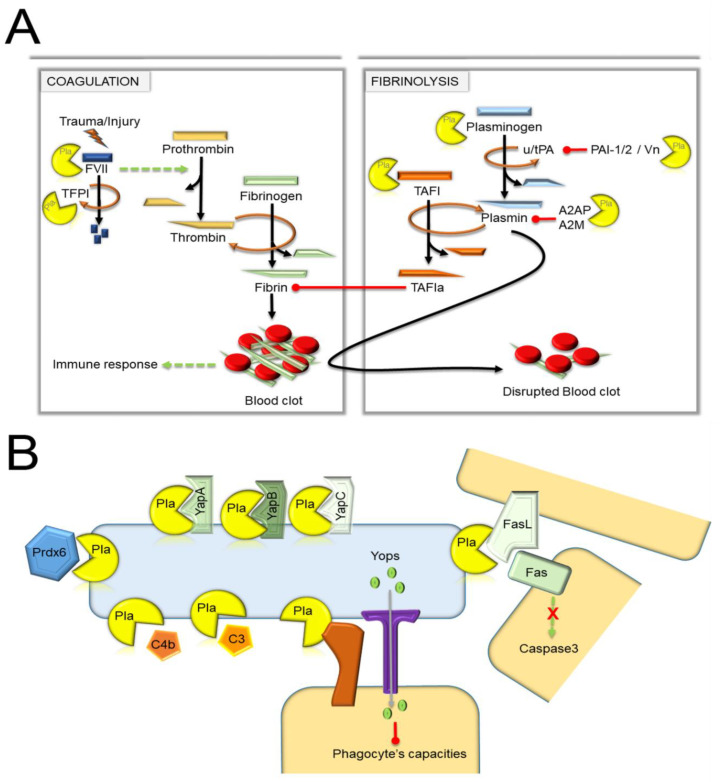
Figure 3.
The different substrates of Pla. (A) Hemostasis cascade. Trauma or an injury activates the coagulation cascade, which leads to the production of a blood clot. The fibrinolysis inhibits the coagulation cascade and disrupts the blood clot. Dashed green and brown circular arrowheads indicate respectively a multiple steps process and a single step leading to protein cleavage. Black arrowheads show the different products of the cleaved protein. Red lines with ball indicate inhibition. Pla (pacman) acts as a protease. (B) The Pla protease cleaves proteins located at the surface of the bacteria (blue cell) and the host’s cell (yellow) or other host’s proteins. Pla also acts as an adhesin (independently of its proteolytic activity), which triggers the secretion of Yops into the host’s cell cytoplasm and inhibits the phagocyte’s ability to kill the bacteria and induce an immune response. Redline with ball indicates inhibition; dashed green arrowhead, a multiple-step process leading to caspase 3 activation; red-cross, inhibition.