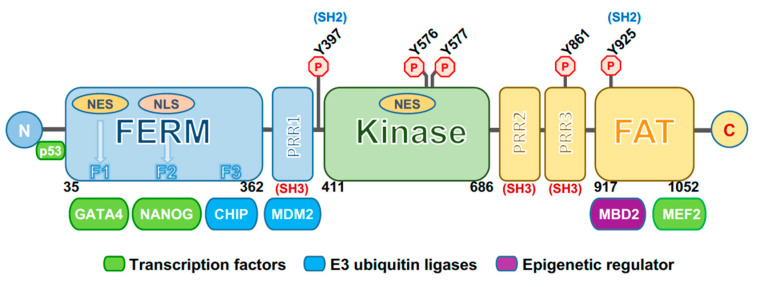
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK). The three main domains of FAK are depicted: The N-terminal 4.1, ezrin, radixin, moesin homology domain (FERM) (in blue), central kinase domain (in green), and focal-adhesion targeting (FAT) domain (in yellow). Domain boundaries are shown. F1, F2, and F3 represent the three lobes of the FERM domain and the regions for binding with transcription factors (such as GATA4 and NANOG) and E3 ubiquitin ligase factors (such as CHIP). Other binding sites are those for MDM2 (E3 ubiquitin ligase), MBD2 (methyl-CpG binding domain protein 2, an epigenetic factor) and MEF2 (transcription factor). Outside the FERM domain the p53-binding site is shown. A nuclear localization sequence (NLS) is located at the F2 FERM lobe, while two nuclear export sequences (NES) are at the F1 FERM lobe and in the kinase domain. PRR1, 2, and 3 represent proline-rich regions (i.e., two polyproline (PxxP) motifs) that interact with the Src homology SH3 domains of several proteins, including Src. Several phosphorylation sites are depicted, among which include Y397, the autophosphorylation site, and Y925, both binding sites for Src. N: N-terminus. C: C-terminus.