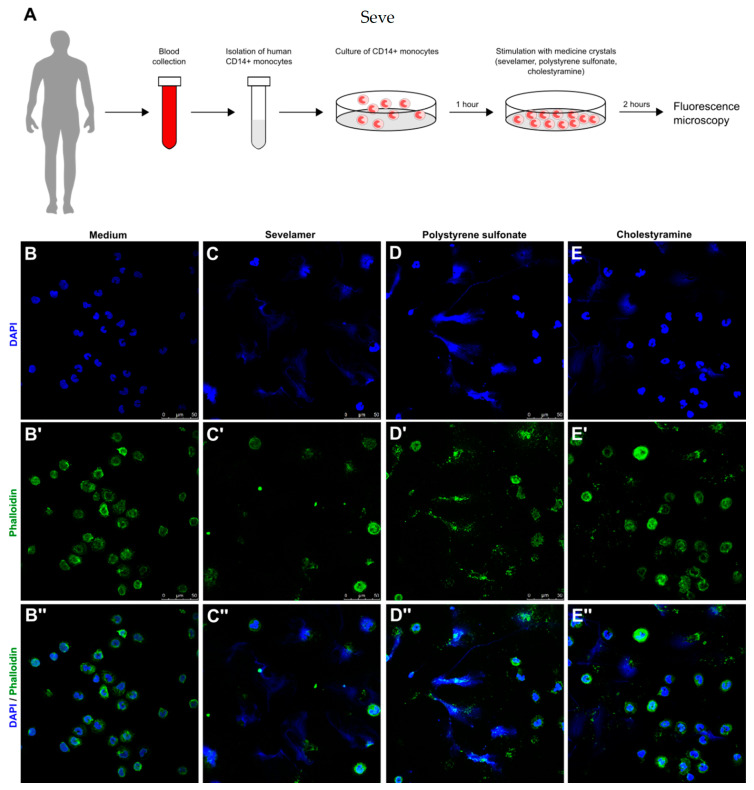
Figure 6.
Crystals of ion-exchange resins induce extracellular trap formation in human CD14+ monocytes. (A) Schematic showing work flow. Human blood CD14+ monocytes were isolated from healthy individuals and stimulated with or without sevelamer, polystyrene sulfonate, or cholestyramine crystals (1000 µg/mL) for 2 h. (B–E) After stimulation, CD14+ monocytes were stained with DAPI (blue, stains nuclei) (B–E) and phalloidin (green, stains actin) (B’–E’) to visualize extracellular trap formation in response to sevelamer (C), polystyrene sulfonate (D), and cholestyramine (E) crystals or the medium (control) (B). Images are also shown as a merge of DAPI and phalloidin (200× magnification (B’’–E’’)).