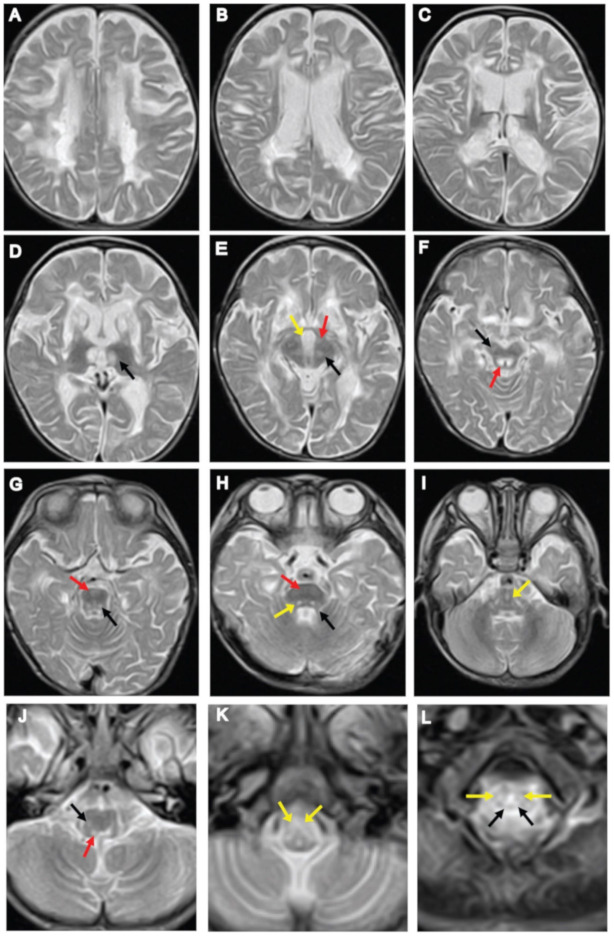
Figure 1.
Neuroimaging findings at three years of age. (A–C) Axial T2-weighted images of brain MRI showing signal abnormalities in the periventricular white matter, putamen, caudate nucleus, splenium of the corpus callosum, and anterior and posterior limb of the internal capsule. (D) Symmetrical bilateral areas of increased signal intensity in the medial thalamic nucleus (black arrow). (E,F) Axial T2-weighted images of the midbrain: (E) interpeduncular cistern (yellow arrow), cerebral peduncle (red arrow), substantia nigra (black arrow); (F) substantia nigra (black arrow) and periaqueductal region (red arrow). (G–I) T2-weighted images of the pons: (G) pyramidal tract (red arrow), pontine tegmentum (black arrow); (H) superior cerebellar peduncle (black arrow), pyramidal tract (red arrow), pontine tegmentum (yellow arrow); (I) diffuse hyper-intensive lesions in the medial lemniscus (yellow arrow). (J,K) T2-weighted images of the medulla oblongata shows abnormal intensities in the medullary tegmentum, spinocerebellar tracts, and pyramids: (J) medullary tegmentum (red arrow), spinocerebellar tract (black arrow); (K) pyramids (yellow arrow). (L) T2-weighted images of the upper cervical spinal cord revealed abnormal intensity within the lateral corticospinal tracts (yellow arrows) and the dorsal columns (black arrows).