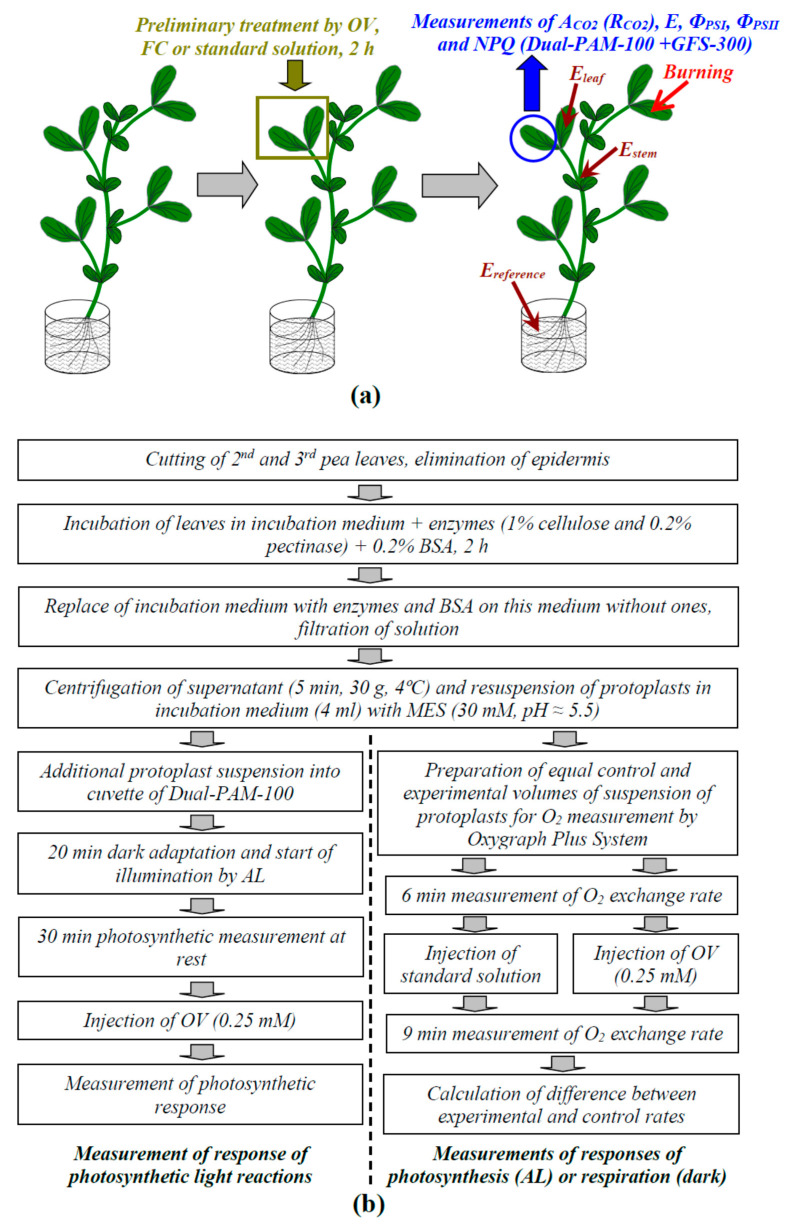
Figure 11.
(a) Schema of investigations of the influence of the preliminary modification of the activity of H+-ATPase in the plasma membrane on electrical signal-induced photosynthetic and respiratory responses. Activity of H+-ATPase was decreased by leaf treatment with sodium orthovanadate (OV) and increased by treatment with fusicoccin (FC). The preliminary OV (0.5 mM) and FC (1 µM) treatments of the second mature leaves in seedlings was performed by incubation of the leaf (2 h) in solutions of these chemical agents. After that, these leaves were dried using filter paper and used for extracellular measurement of photosynthetic and electrical activities. OV and FC were dissolved in standard solution (1 mM KCl, 0.5 mM CaCl2, and 0.1 mM NaCl). Similar treatment using the standard solution was used as the control. The arrows mark the local burning of the first mature leaf (flame, 2–3 s). Eleaf and Estem are the measuring electrodes that were placed on the second leaves (center of leaflet) and stems near these leaves, respectively; Ereference is the reference electrode. (b) Schema of experiments using a suspension of protoplasts from pea leaves. Photosynthetic light reactions were investigated under actinic light (AL, 460 nm, 239 µmol m−2 s−1) using a Dual-PAM-100. O2 exchange rate was investigated under AL (for photosynthetic investigations) or under dark conditions (for respiratory investigations) using an Oxygraph Plus System. The standard solution included 1 mM KCl, 0.5 mM CaCl2, and 0.1 mM NaCl.