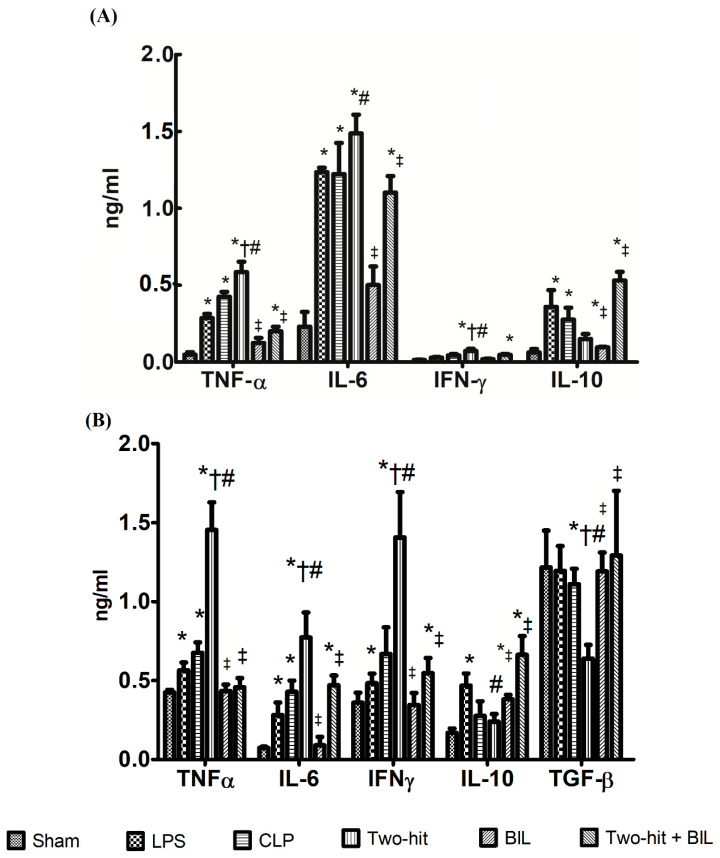
Figure 2.
Bilirubin effects on the expression of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the (A) plasma; (B) lung of the “two-hit” sepsis model. Mice were administered i.p. LPS at 5 mg/kg body weight on day 0. After 24 h, the mice were challenged with cecal ligation and puncture (CLP: 25-gauge needle and double-puncture). Next, the mice were administered bilirubin at 30 mg/kg body weight. The levels of pro-inflammatory (TNF-α, IL-6, IFN-γ) and anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10 and TGF-β) were determined by ELISA after one day. Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 5 mice per group) and analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey–Krammer multiple comparison test using the SPSS program. * p < 0.05 versus sham. # p < 0.05 versus LPS. † p < 0.05 versus CLP. ‡ p < 0.05 versus “two-hit”. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-6, and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), interleukin IL-10 and transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β). LPS: lipopolysaccharide, CLP: cecal ligation and puncture, BIL: bilirubin.