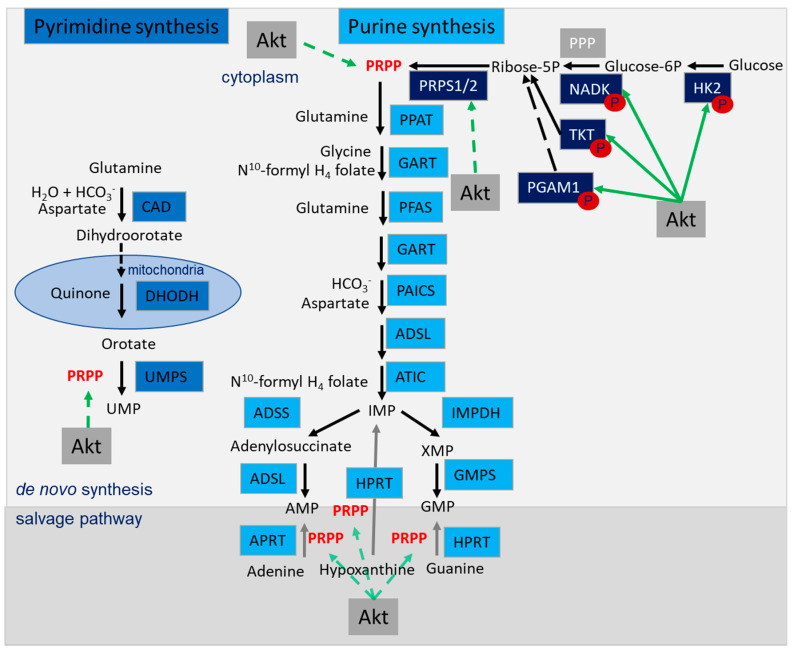
Figure 3.
Nucleotide synthesis pathway: de novo synthesis of pyrimidines and purines and salvage pathway, utilizing phospho-ribose pyrophosphate (PRPP) produced in Akt-regulated pathways to generate uridine monophosphate (UMP), adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and guanosine monophosphate (GMP). Enzymes of the pyrimidine synthesis in light blue, enzymes of the purine synthesis in turquoise, enzymes involved in generating PRPP in dark blue. Akt-dependent activation is marked with green arrows, the metabolic pathway of de novo synthesis is marked with black arrows and the salvage pathway is marked with grey arrows. Abbreviations: pyrimidine synthesis: carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase (CAD), dihydroorotase, dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH), uridine monophosphate synthetase (UMPS); purine synthesis: adenylosuccinate lyase (ADSL), 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide formyltransferase (ATIC), glycinamide ribonucleotide transformylase (GART), phosphoribosylaminoimidazole carboxylase and phosphoribosylamino-imidazolesuccinocarboxamide synthase (PAICS), phosphoribosyl-formylglycinamidine synthase (PFAS), phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate amidotransferase (PPAT); the salvage pathway: adenylosuccinate synthase (ADSS), adenine phosphoribosyltransferase (APRT) guanine monophosphate synthase (GMPS), hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase (HPRT), inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH); generation of PRPP; hexokinase 2 (HK2), NAD kinase (NADK), phosphoglycerate mutase 1 (PGAM1), pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), ribose-phosphate pyrophosphokinase 1/2 (PRPS1/2), transketolase (TKT).