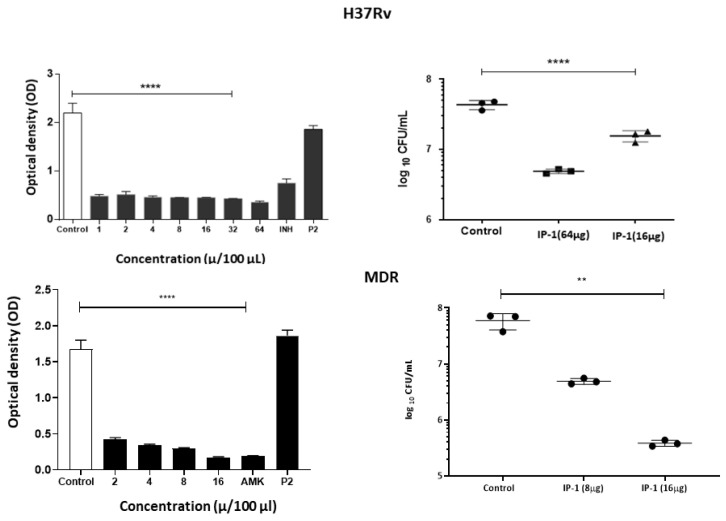
Figure 6.
Effect of IP-1 against M. tuberculosis (top panel H37Rv, bottom panel MDR strain) in vitro. Left figures show the MICs determined by broth microdilution evaluated by a colorimetric assay using Cell Titer 96® Aqueous, and right figures show viability of the bacteria by counting the colony-forming units after treatment with the indicated IP-1 concentrations; each symbol (Triangles, squares, circles) represent an independent determination. All the IP-1 concentrations showed significant activity against mycobacteria, being MDR strain more susceptible to IP-1 and similar to the MIC control that corresponded to amikacin (AMK), an antibiotic for which this strain is highly susceptible, and for drug-sensible H37Rv strain isoniazid (INH) that is the most efficient primary antibiotic. As negative control we include P2, a synthetic peptide derived from arachnid AMP at 64 μg. Each result is reported as the mean ± SD, asterisk represents statistical significance (** p < 0.003, **** p < 0.0005).