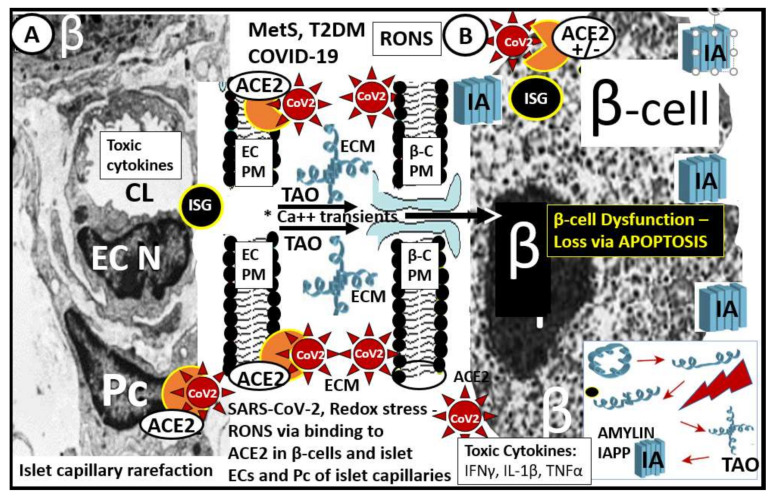
Figure 2.
Pancreatic islet β-cells undergo a multiple hit injury with MetS/T2DM and COVID-19. This illustration depicts the close relationship of the islet capillaries and the β-cells with transmission electronic microscopic (TEM) images of the pancreatic islet capillary Panel (A) and the β-cell Panel (B) in those infected by SARS-CoV-2. Panel (A) depicts an islet capillary in close proximity to an islet β-cell (preclinical HIP rodent model) and notes that CoV-2 may bind not only to the endothelial cell ACE2 protein of capillary endothelial cells but may also bind to pericytes, since ACE2 has recently been found to bind to pericytes in the brain and myocardial capillary specimens especially if the EC glycocalyx barrier function has been damaged allowing SARS-CoV-2 to enter the subendothelial space. Panel (B) illustrates the small electron dense dots that are the insulin secretory granules (ISG) within the β-cell cytoplasm (preclinical HIP rodent model). Additionally, amylin undergoes unfolding and misfolding to form islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP) (panel (B)—lower right hand) when exposed to toxic oxidative stress—reactive oxygen and nitrogen (nitrosative stress) species (RONS). The early more intermediate-sized toxic amyloid oligomers (TAO) of amylin have a propensity to form membrane permeant channels in the islet β-cell plasma membrane, which allow for the entrance of calcium transients to enter the β-cell and result in not only β-cell dysfunction but also β-cell loss via apoptosis see reference 63 and 64. There is approximately a 50% decrease in β-cell function of those with T2DM and a 40–50% loss of β-cells in individuals with impaired glucose tolerance or prediabetes. Therefore, one can deduce that if there is already this much β-cell loss why SARS-CoV-2 could significantly add to this loss via SARS-CoV-2 binding to the ACE2 on β-cells (+/−) with further β-cell dysfunction, apoptosis and possibly accelerate the natural history of T2DM. Note the (+/−) regarding the presence of the ACE2 enzyme receptor since there is currently some controversy regarding its presence in pancreatic islet β-cells; see Section 6 reference [70,71,72,73]. Notably, systemic toxic cytokines liberated from pulmonary tissues and systemic immune cells can also be related to pancreatic islet injury mechanisms. Additionally, in preclinical T2DM rodent models, there is intra-islet capillary rarefaction that may contribute to β-cell dysfunction and death see reference 66. ACE2 = angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (orange color); β = β-cell; β-C = β-cell; Ca++ = calcium; CoV-2 = SARS-CoV-2 (spiked red icon); CL = capillary lumen; EC = endothelial cell; ECM = extracellular matrix; IA = islet amyloid; IAPP = islet amyloid polypeptide deposition (blue fibril icon); IFN-γ = interferon gamma; Il-1β = interleukin 1 beta; ISG = insulin secretory granules; MetS = metabolic syndrome; N = nucleus; Pc = pericyte; PM = plasma membrane; RONS = reactive oxygen and nitrogen (nitrosative stress) species; TAO = toxic intermediate-sized amyloid oligomers; TNFα = tumor necrosis alpha; T2DM = type 2 diabetes mellitus.