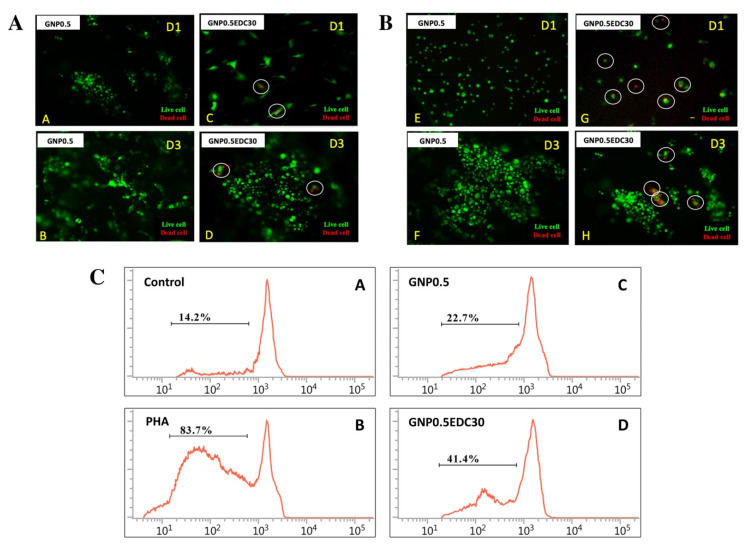
Figure 5.
Effects of crosslinking on human epidermal keratinocytes (HEK) and dermal fibroblasts (HDF). Live/dead assay indicated the EDC crosslink scaffolds were toxic towards skin cells compared to genipin (GNP) and dihydrothermal (DHT) crosslink scaffold. (A) HDF cells and (B) HEK cells seeded on GS crosslink with GNP0.5/GNP0.5EDC30 at day 1 (D1) until day 3 (D3) (100X magnification). The white line circle indicates the dead cells. Effects of crosslinking on immunogenicity. (C) Proliferation properties of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) in medium supplemented with GS extracts in the carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester (CFSE)-labeling assay. (A–D) Representative FACS histograms of immune cells cultured with supplemented medium. Proliferation response without GS extracts was used as a control. PHA served as a positive control. PHA = phytohemagglutinin. The depicted line defines the level of proliferated immune cells. Results revealed that double crosslinking resulted in significant immune reaction in vitro. * p < 0.05 tested with Student’s t-test.