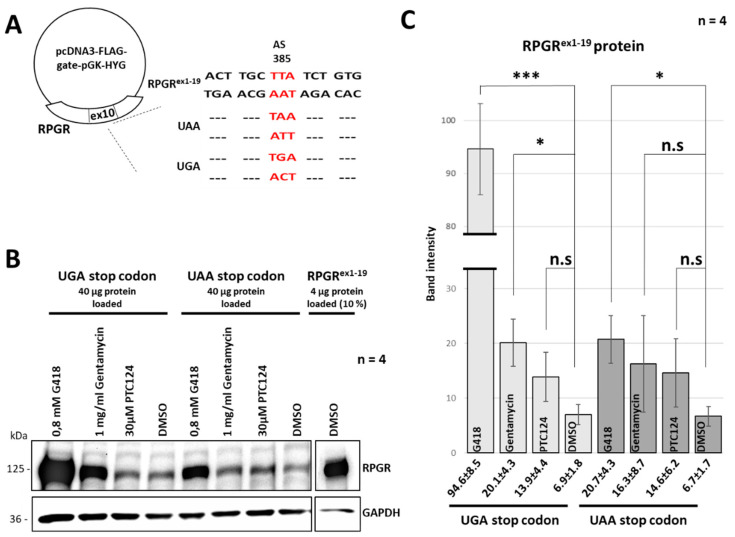
Figure 3.
PTC124 treatment partially restores RPGR expression. (A) RPGR expression constructs encoding the full-length RPGR protein encoded by exon 1 through 19. Expression constructs were mutated with either an UAA stop codon (RPGR- UAA stop codon) or a UGA stop codon (RPGR- UGA stop codon) at amino acid position 384. The RPGR expression construct encoding the reference RPGRex1–19 protein was used as a control. Sequence alterations in the expression construct are highlighted in red. (B) RPGR expression constructs were transfected into HEK293T cells and treated with either a single dose of PTC124, G418, Gentamycin or DMSO for 48 h. Full-length RPGR was detected applying a polyclonal RPGR antibody directed against amino acids 379 to 509 of RPGR. The treatments with G418 and gentamycin partially restored the full-length RPGR protein expression. Read-through efficacies of the reagents PTC124, G418 and gentamycin were compared to samples incubated with DMSO. The experiments were replicated four times (n = 4). GAPDH (36 kDa) was used as a loading control. Protein sizes are indicated on the left side in kDa. (C) Quantification of the band intensities suggested that all read-through-inducing reagents led to an upregulation of the expression of full-length RPGR protein. Levels were normalized to GAPDH signal intensities and compared to the negative control (DMSO). The quantification was based on four independent replicates (n = 4). Error bars represent standard deviation. Asterisks: significant differences; n.s: non-significant, *: p ≤ 0.05, ***: p ≤ 0.001.