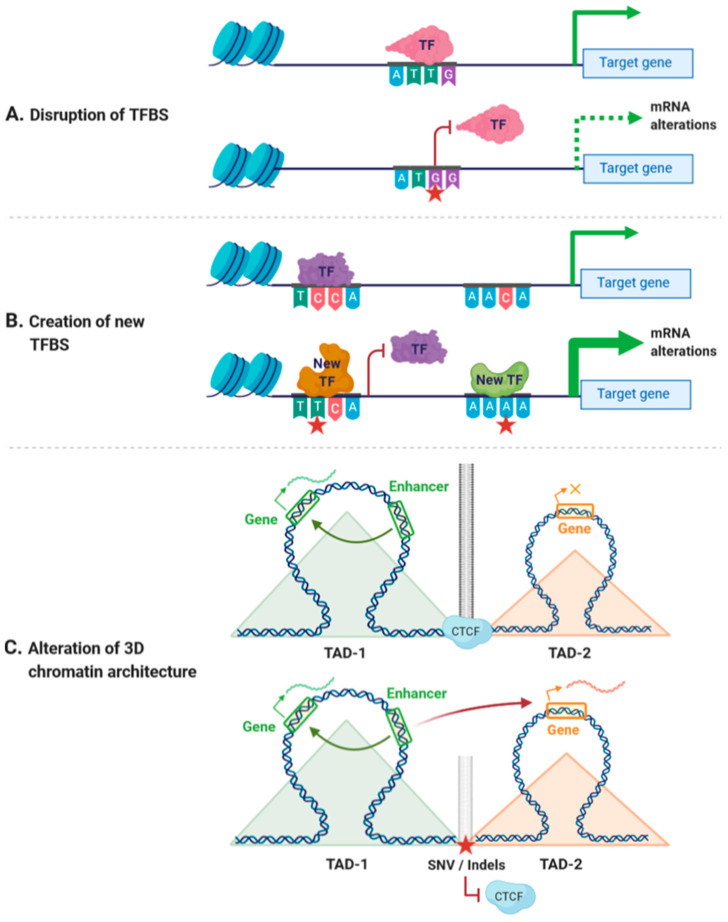
Figure 1.
Effects of cis-regulatory variants. (A) Variants within cis-regulatory regions can disrupt transcription factor binding sites (TFBSs), leading to decreased mRNA expression. (B) Variants within cis-regulatory regions can create new TFBSs and generate new regulatory pathways. (C) Variants affecting the binding of CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF) can disrupt insulator activity between two topological associating domains (TADs), generating new enhancer–promoter interactions that may lead to altered expression of genes within these TADs. Red star indicates the position of a new single nucleotide variant (SNV) or an insertion/deletion (Indel). Orange × indicates inhibition of gene expression.