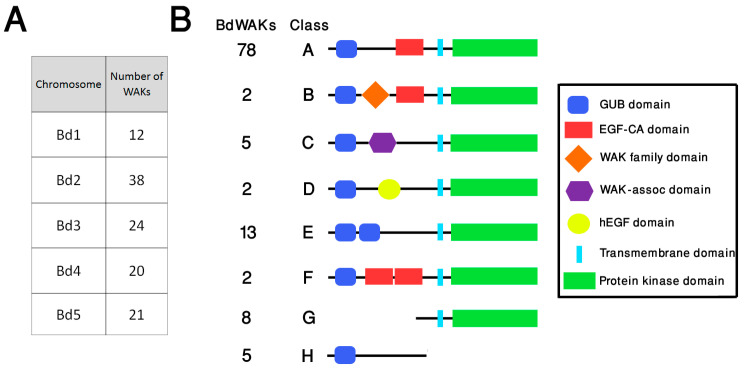
Figure 1.
Organisation and structure of WAK members in B. distachyon (A) Distribution of BdWAK genes on B. distachyon chromosomes. (B) Schematic representation of eight structural classes (A–H) of WAK proteins identified in B. distachyon. The number of BdWAKs identified for each class is indicated. The eight classes have varying motifs and motif organisation with Class A considered the typical WAK structure and Class B through Class H considered ‘non-typical’ WAK structures. Class A: typical WAK structure with a GUB (galacturonan-binding) domain, an EGF-Ca (epidermal growth factor-like calcium-binding) domain, and a kinase domain; Class B: as for Class A, but with a WAK family domain present between the GUB and EGF-Ca domains; Class C: a WAK-associated domain is present after the GUB domain and there is no EGF-Ca domain; Class D: a variant on the Class C structure with a hEGF domain present instead of the EGF-Ca domain; Class E: contains a duplication of the GUB domain and lacks the EGF-Ca domain; Class F: contains a duplication of the EGF-Ca domain between the GUB and protein kinase domains.; Class G is a truncated protein with only a protein kinase domain; Class H is a truncated protein with only the extracellular GUB domain.