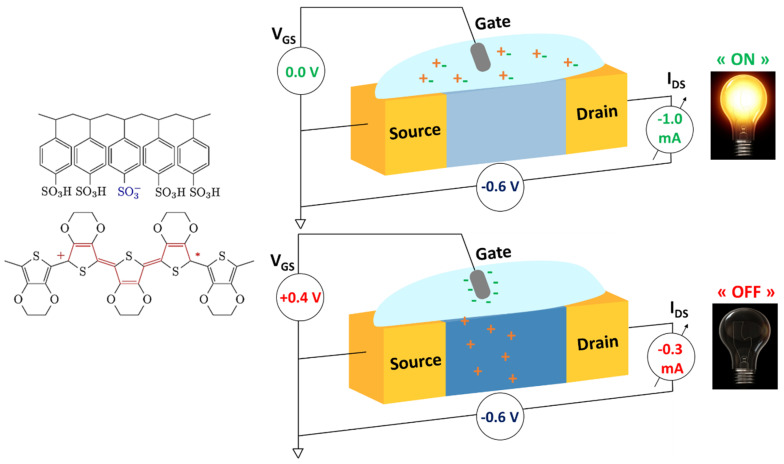
Figure 1.
Schematic of an organic electrochemical transistor (OECT). A bias voltage (VDS) is applied between two electrodes, source and drain, which are connected by a channel made of an organic semiconductor, e.g., p-type poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) doped with polystyrene sulfonate (PEDOT:PSS). This channel is in contact with an electrolyte where a third electrode is immersed, the gate electrode, VG, (i.e., Ag/AgCl electrode). (Top): In the absence of a gate voltage, the channel is in its conductive (oxidized) state; this is the “on” state of the device. (Bottom): Application of a positive voltage results in reduction of the channel material (neutral state), switching the device to the “off” state.